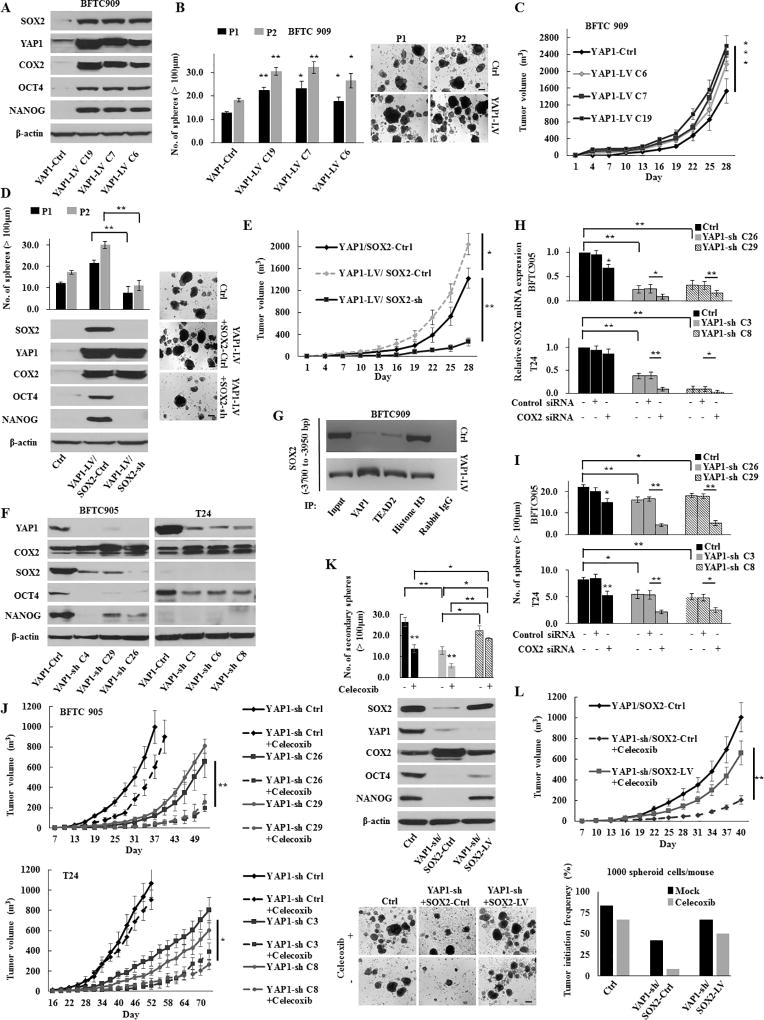
Figure 3.
The YAP1-SOX2 signaling axis in urothelial CSCs. (A) Western blotting in stable BFTC 909 YAP1-induction (YAP1-LV) cells. YAP1 induction increased the expression of SOX2 and COX2. (B) Sphere formation and self-renewal assays through the second (P2) passage from the first passage (P1) in YAP1-LV cells. Representative images of sphere formation (scale bars, 200 µm) were shown. (C) In vivo tumorigenesis of stable YAP1-LV cells (four mice per group). (D) Sphere formation and self-renewal assays (left upper) and western blotting (left lower) in BFTC 909 YAP1-LV or YAP1-Ctrl cells transduced with SOX2-LV or SOX2-Ctrl (YAP1-Ctrl/SOX2-Ctrl, YAP1-LV/SOX2-sh, and YAP1-LV/SOX2-Ctrl). Right, representative images of sphere formation (scale bars, 200 µm). (E) In vivo tumorigenic effect of SOX2 knockdown in stable BFTC 909 YAP1-LV cells (YAP1-LV/SOX2-sh). (F) Western blotting in YAP1 knockdown (YAP1-sh) cells. (G) ChIP assays conducted on the enhancer region of the SOX2 gene using the indicated antibodies in BFTC 909 YAP1-LV or YAP1-Ctrl cells. TEAD is a main transcription factor partner for YAP1 recruitment to chromatin. Histone H3 was used as the positive control and normal rabbit IgG was used as the negative control for immunoprecipitation. (H) The relative expression of SOX2 72 h after transfection with COX2 siRNA in YAP1-sh cells. The dual inhibition of COX2 and YAP1 significantly repressed the SOX2 expression compared with either inhibition alone. (I) A sphere formation assay in YAP1-sh cells transfected with COX2 siRNA. (J) In vivo tumorigenesis of stable YAP1-sh cells in the presence or absence of celecoxib treatment (four mice per group). (K) Sphere formation assay (upper) and western blotting (middle) in BFTC 905 YAP1-sh or YAP1-Ctrl cells transduced with SOX2-sh or SOX2-Ctrl (YAP1-Ctrl/SOX2-Ctrl, YAP1-sh/SOX2-LV, and YAP1-sh/SOX2-Ctrl). Lower, representative images of sphere formation (scale bars, 200 µm). (L) In vivo tumorigenic and tumor initiation effects of SOX2 induction in BFTC 905 cells with the dual inhibition of YAP1 and COX2. Upper, mice injected with stable YAP1-sh/SOX2-LV cells were treated with celecoxib (five per group); Lower, tumor initiation frequency of diluted spheroid cells (1,000 cells/injection). After the injection of cells, mice were treated with mock or celecoxib (12 per group).
Each error bar indicates mean ± SEM. *, P <0.05; **, P <0.01 (Wilcoxon–Mann–Whitney test [B, C, and J] and Kruskal–Wallis with post-hoc test [D, E, H, I, K, and L]).