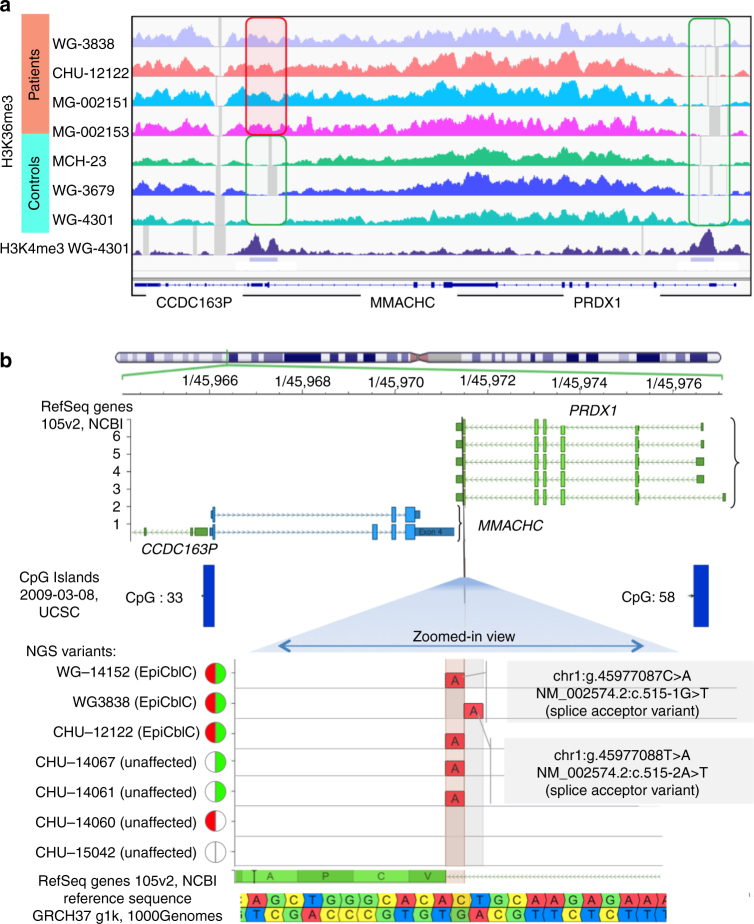
Fig. 4.
The MMACHC epimutation is associated with a H3K36me3 chromatin mark in the promoter and a mutation in the PRDX1 adjacent gene. a Results of ChIP-Seq analyses at the genomic region encompassing the promoters of MMACHC/CCDC163P and PRDX1. Genomic panels show normalized coverage for histone H3 trimethylated lysine 36 (H3K36me3) mark in patients (tracks 1–4 from top) and controls (tracks 5–7). H3K4me3 track along with the peak calls, for one of the controls, has also been shown. The rectangles indicate the promoter regions. The same scale has been set in all panels. See Methods for more details on samples and analysis. b Identification of PRDX1 splice acceptor variants in cases with MMACHC epimutation by whole-genome sequencing. Top: the vertical black line is positioned on the locus of the two PRDX1 variants within the splice acceptor site (AG sequence) on intron 5. Bottom: zoomed view centered on the splice acceptor site of PRDX1 intron 5. Genomic positions are reported according to the reference sequence GRCh37. The red semicircle denotes the presence of MMACHC genetic mutation. The green semicircle denotes the presence of MMACHC epimutation. The white semicircle denotes the absence of both