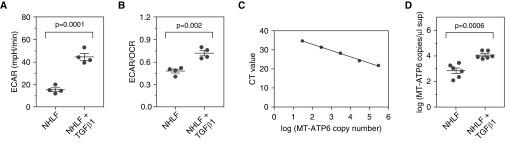
Figure 1.
Transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1)–stimulated normal human lung fibroblasts (NHLFs) show altered metabolism and high concentrations of extracellular mitochondrial DNA. (A and B) NHLFs stimulated with 5 ng/ml of TGF-β1 for 7 days (right) demonstrated the previously reported increase in glycolysis relative to unstimulated cells (left) as measured by significant elevations in (A) extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) and (B) ratio of ECAR to oxygen consumption rate (OCR). Data are presented as mean ECAR (mpH/min) and mean (±SEM) ratio of ECAR to OCR, respectively. (C) A standard curve was developed from serial dilutions of a commercially available plasmid containing the sequence of the human MT-ATP6 gene. (D) Relative to supernatants obtained from NHLFs cultured with normal medium (left), the mean MT-ATP6 copy number is significantly increased in the supernatant of NHLFs stimulated with 5 ng/ml of TGF-β1 for 7 days (right). Data are presented graphically as log base 10 of the raw values (MT-ATP6 copies per microliter of supernatant) with mean ± SEM. A graph including the raw values is presented in Figure E2D. CT = cycle threshold.