Figure 3.
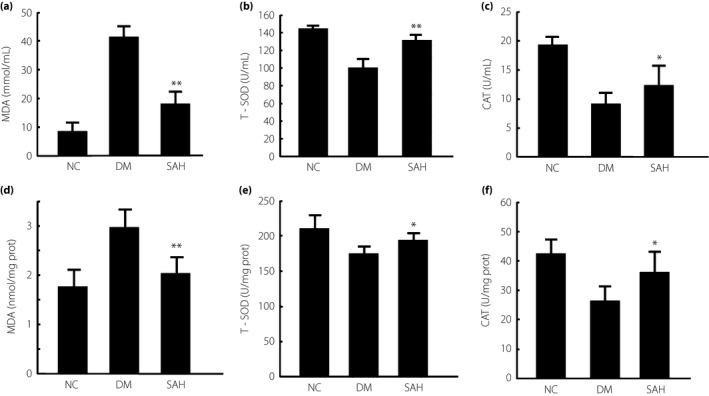
Levels of malondialdehyde (MDA), total superoxide dismutase (T‐SOD) and catalase (CAT) activity in the plasma and kidney of mice with diabetes mellitus (DM) induced by a high‐fat diet and a low dose of streptozotocin. Subcutaneous administration of hydrogen gas (H2) to the mice (a) decreased the levels of MDA, and promoted the activities of (b) T‐SOD and (c) CAT in plasma. After 4 weeks of H2 treatment, the plasma samples from each group were collected to detect the levels of indicators for plasma oxidative stress. The oxidative stress was significantly reduced in the subcutaneous administration of H2 group (SAH) group compared with the DM group. Subcutaneous administration of H2 (d) reduced the content of MDA and promoted the activities of (e) T‐SOD and (f) CAT in the kidney. Renal tissues were homogenized to examine T‐SOD and CAT activity, and MDA content. bicinchoninic acid assay was used to determine protein levels in renal samples to normalize oxidative parameters. The data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 8–16). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. NC, normal control group.
