Figure 4.
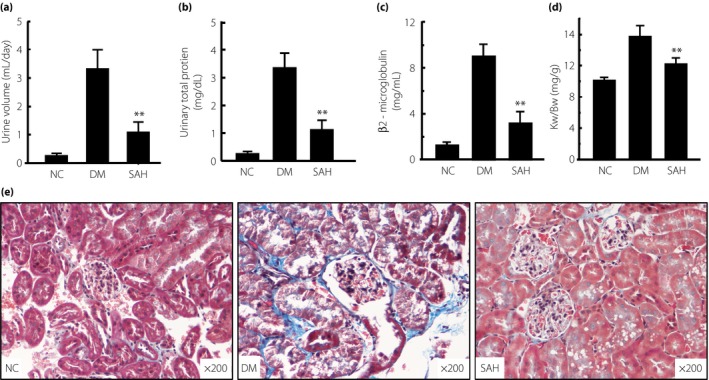
Subcutaneous administration of hydrogen gas (H2) reduced 24‐h urine volume, urinary total protein, β2‐microglobulin, kidney weight/bodyweight ratio (Kw/Bw) and renal fibrosis resulting from diabetes. After 4 weeks of H2 treatment, (a) 24‐h urine volume, (b) urinary total protein, (c) β2‐microglobulin and (d) Kw/Bw were detected, and (e) kidney tissues were fixed for Masson staining. The 24‐h urine volume, urinary total protein, β2‐microglobulin, Kw/Bw and renal fibrosis in the group with H2 treatment were significantly reduced, compared with the diabetes mellitus (DM) group (n = 16 for each group). The data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 8–16). **P < 0.01. NC, normal control group; SAH, subcutaneous administration of H2 group.
