Figure 2.
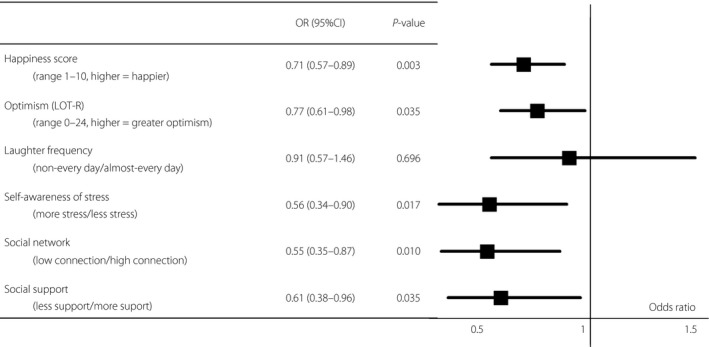
Odds ratios (OR) for diabetic nephropathy of six indicators of psychosocial factors adjusted for age and sex. Logistic regression analysis was carried out to evaluate whether psychosocial factors were significantly associated with an increase in the risk of diabetic nephropathy. The threshold of statistical significance was defined as P < 0.05. The OR of ‘happiness score’ and ‘optimism’ are shown as per 1 standard deviation. In the logistic regression analysis adjusted for age and sex, a high happiness score (OR per 1 standard deviation 0.72, 95% CI: 0.57–0.90, P = 0.004), high LOT‐R score (OR per 1 standard deviation 0.79, 95% CI: 0.62–0.99, P = 0.044), less self‐awareness of stress (OR 0.59, 95% CI: 0.36–0.94, P = 0.028), high connection of social network (OR 0.57, 95% CI: 0.37–0.90, P = 0.015) and more social support (OR 0.61, 95% CI: 0.38–0.96, P = 0.042) were associated with reduced risk of presence of diabetic nephropathy. CI, confidence interval; LOT‐R, Life Orientation Test‐revised; OR, odds ratio.
