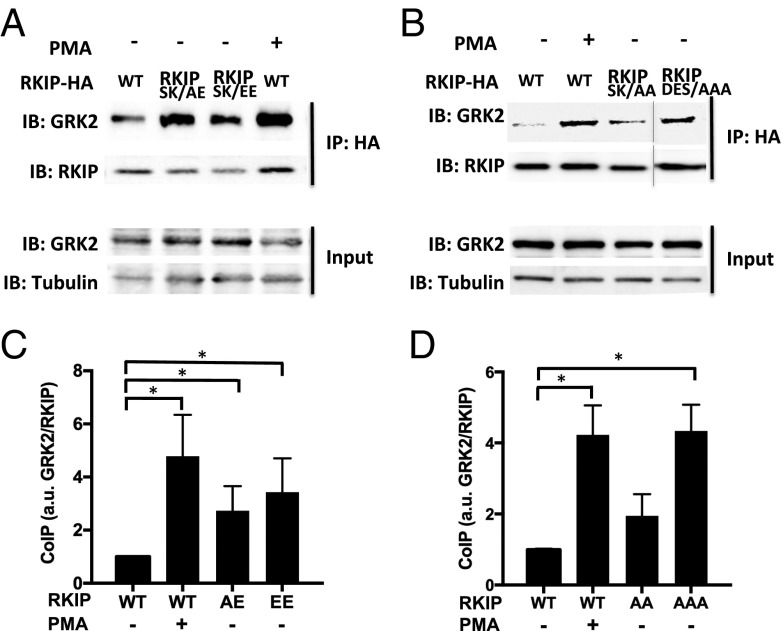
Fig. 3.
In vivo interactions between GRK2 and salt-bridge mutants of RKIP. (A and B) Cells expressing WT HA-RKIP or HA-RKIP variants were incubated with or without PMA (1 μM) for 10 min before precipitation with an anti-HA antibody and blotted for GRK2. Input represents 10% of total lysates used for immunoprecipitation assays: Representative coimmunoprecipitation assays using RKIP mutants (A) S153A/K157E (SK/AE) or S153E/K157E (SK/EE) or (B) S153A/K157A (SK/AA) or D134A/E135A/S153A (DES/AAA) are shown. (C and D) Plots of GRK2 bound to RKIP mutants: S153A/K157E (AE); S153E/K157E (EE); S153A/K157A (AA); D134A/E135A/S153A (AAA). Average of blot densities for GRK2 normalized to RKIP using (C) four or (D) three independent experiments including A is shown. Error bars indicate SEM. *P < 0.05 by a one-tailed Student’s t test.