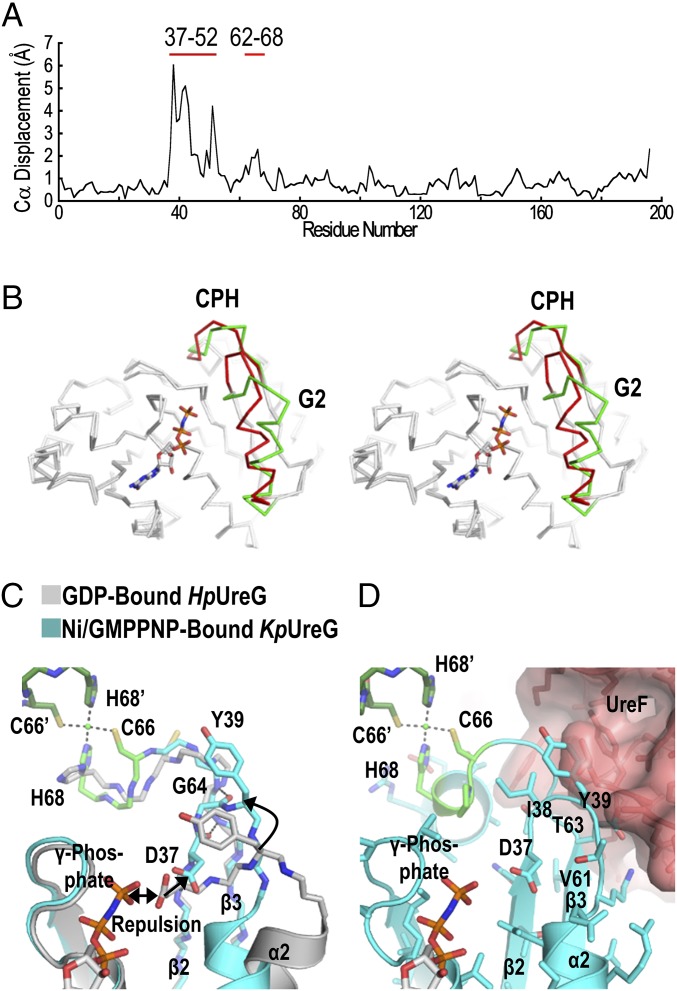
Fig. 2.
Conformational changes of UreG upon GTP binding. (A) The structures of the GDP-bound HpUreG (4HI0, chain F) and the Ni/GMPPNP-bound KpUreG (5XKT, chain A) were superimposed and values of Cα displacement were plotted. (B) Stereodiagram highlighting significant conformational changes found in the G2 region (residues 37–52) and near the CPH metal-binding motif (residues 62–68), which are colored in green and red for the GDP-bound HpUreG and the Ni/GMPPNP-bound KpUreG, respectively. (C) Charge–charge repulsion between Asp37 and the γ-phosphate group elicits conformational changes that are propagated to the CPH metal-binding site. The repulsion pushes the Asp37 away from the nucleotide-binding site so that Asp37 and Ile38 (β2 strand) form backbone hydrogen bonds with Val61, Thr63, and Gly64 (β3 strand). This zip-up motion of the β2 and β3 strands propagates conformational changes to the CPH metal-binding motif and causes helix-2 to tilt by ∼35° toward the nucleotide-binding site. (D) Moreover, Tyr39 of the G2 region moves toward the UreF2H2-binding site, introducing steric clashes that promote dissociation of UreG from the UreG2F2H2 complex. Residues from the opposite protomer are indicated by apostrophes.