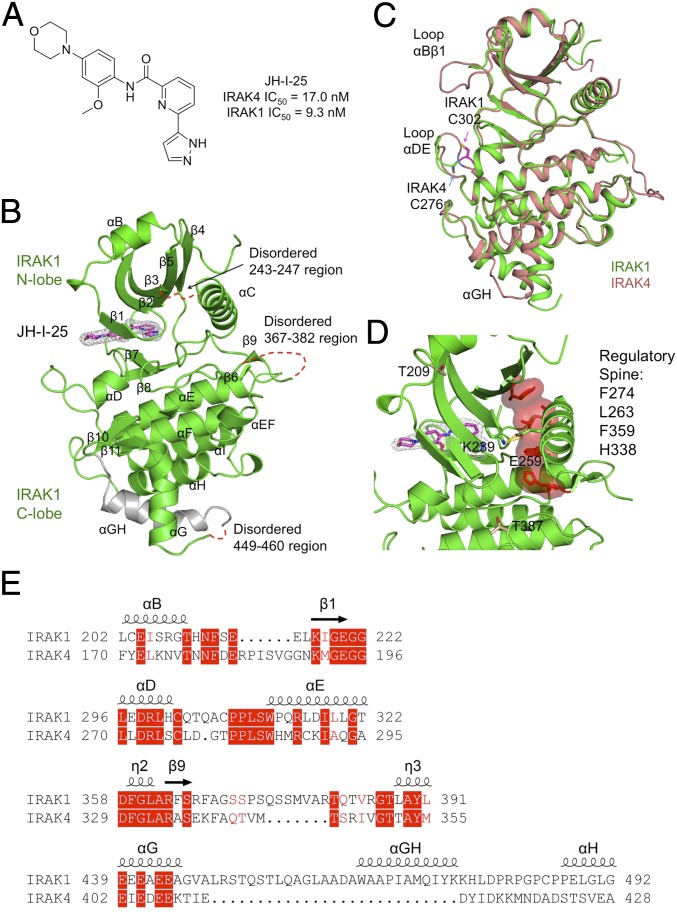
Fig. 3.
Structure of inhibitor-bound IRAK1. (A) Chemical structure of the dual IRAK1/4 inhibitor JH-I-25 used in the cocrystallization. (B) A ribbon diagram of IRAK1 in complex with the inhibitor. The secondary structures are labeled, and the JH-I-25 inhibitor is shown with carbon atoms in magenta, nitrogen atoms in blue, and oxygen atoms in red, superimposed with its electron density in gray. IRAK1 is in green with the exception of the long, gray-colored IRAK1-specific insertion. (C) Superposition between IRAK1 (green) and IRAK4 (pink, PDB ID code 2NRU). The main differences between these two kinase domains at the αBβ1 loop, the αDE loop, and the αGH insertion are labeled. The different locations of C302 of IRAK1 and its sequence-conserved counterpart C276 of IRAK4 are indicated. (D) The regulatory spine and the K239-E259 salt bridge both indicate an active conformation of IRAK1. (E) Sequence alignment between IRAK1 and IRAK4 at four regions with significantly different structures.