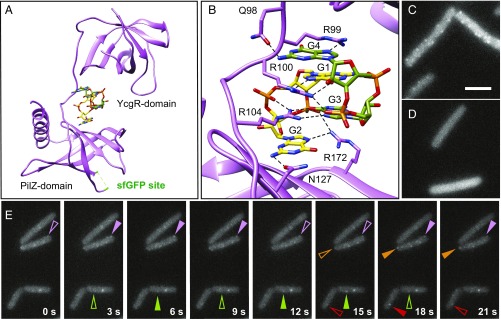
Fig. 4.
MotI-structure–enabled GFP fusion indicates that MotI localizes as transient MotA-dependent puncta. (A) 3D structure of MotI∆4 bound to a dimer of c-di-GMP (c-di-GMP monomer carbons are colored green and yellow, respectively). The locations of the N-terminal YcgR domain, the C-terminal PilZ domain, and the sfGFP insertion site (highlighted green in an unstructured loop in the crystal) are indicated. (B) Enhanced view of MotI residues in contact with the c-di-GMP dimer. Hydrogen bonds are found between E98 and the Watson–Crick edge of guanine base G4, between R99 and the Hoogsteen edge of guanine base G4, between R100 and the Hoogsteen edge of guanine base G1, between the phosphate that connects guanine bases G4 and G3, between R104 and the Hoogsteen edge of guanine base G3, and between N127 and the Watson–Crick edge of guanine base G2. Additionally R99 stacks with guanine base G1, R100 stacks with guanine base G4, and R104 stacks guanine base G2. (C and D) Fluorescence micrograph images taken from a time-lapse series of MotIInh-sfGFP induced with 4 µM IPTG in otherwise wild-type (strain NPS913) (C) and motAE92K (strain NPS915) (D) backgrounds. (Scale bar: 8 μm.) (E) Time-lapse series of fluorescence micrograph images of MotIInh-mNeonGreen induced with 2 µM IPTG (DK5142); images were taken every 3 s. Like-colored carets indicate the same puncta; and transience is indicated by open (waning puncta) and filled (waxing puncta) carets.