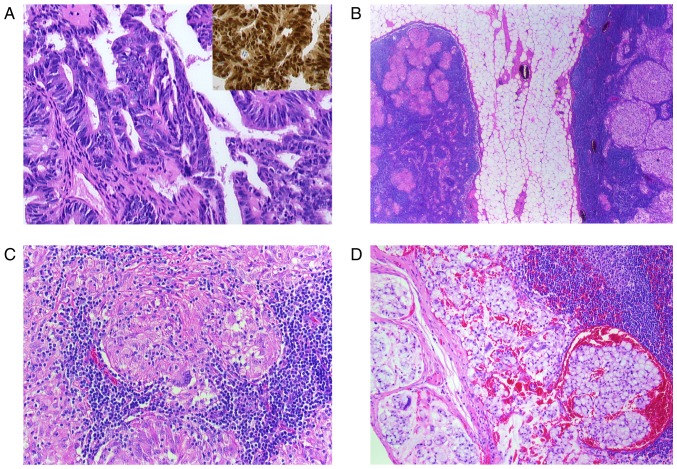
Figure 2.
(A-D) Histological findings of a resected paranasal sinus adenocarcinoma and lymph node. (A) Microphotograph shows the adenocarcinoma with atypical tumor cells (H&E; magnification, ×400) and CDX2 nuclear positive cells, characteristic for intestinal-type adenocarcinoma (inset, H&E, magnification, ×400). (B) Two lymph nodes surrounded by perinodal fat tissue. The right node with noncaseating epitheloid granulomas and the left one with metastatic lesions (H&E, magnification, ×5). (C) Lymph node with noncaseating epitheloid granuloma in higher magnification (H&E, magnification, ×200). Multinuclear giant cells are identifiable. (D) Metastatic carcinoma infiltration in a lymph node (H&E, magnification, ×200). H&E, hematoxylin and eosin; CDX2, caudal type homeobox 2.