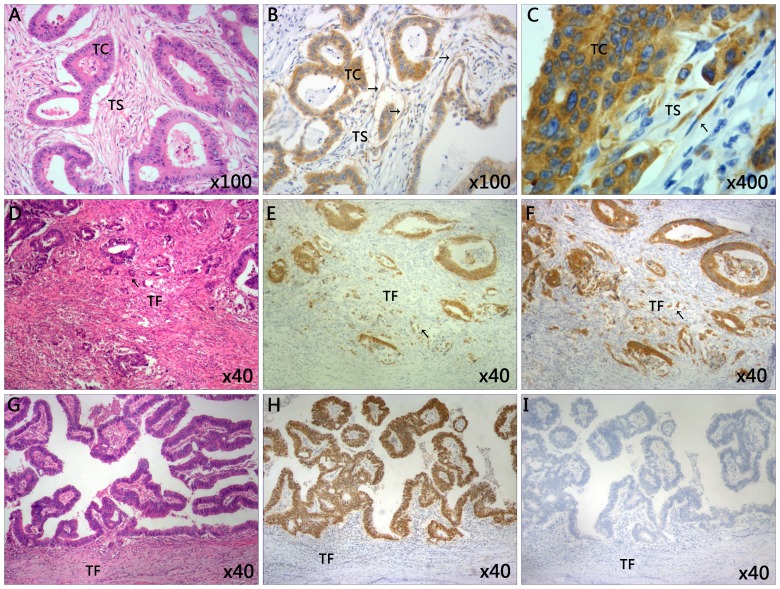
Figure 1.
Representative images of immunohistochemical staining of tissues from patients with CRC. (A) The classic microscopic features of colorectal cancer with hematoxylin and eosin staining. The chromatin in the nucleus was stained violet blue and the cytoplasm and extracellular matrix were stained red. Magnification, ×100. (B) High expression of IMP3 in tumor cells and tumor stroma cells. Magnification, ×100. (C) The IMP3-positive cells in tumor stroma closely resemble spindle cells. Magnification, ×400. (D) High grade of tumor budding stained with hematoxylin and eosin in the TF. Magnification, ×40. (E) The present study observed the tumor buds using CDX2 staining. CDX2 stained the nucleus brown. The mean number of buds was counted using ten high power fields. Specimens were divided into two groups according to the average number of buds: Low grade (≤10 buds) and high grade (>10 buds). Here the image revealed the high grade tumor budding with CDX2 staining in the TF. Magnification, ×40. (F) High expression of tumor budding stained with IMP3 in tumor front of CRC. Magnification, ×40. (G) Low grade tumor budding with hematoxylin and eosin staining in the TF. Magnification, ×40. (H) Low grade of tumor budding stained with CDX2 in tumor front of CRC. Magnification, ×40. (I) Negative expression of IMP3 in tumor tissue and tumor front. Magnification, ×40. Slides A, D and G were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. CDX2, caudal type homeobox 2; CRC, colorectal cancer; IMP3, insulin-like growth factor II mRNA-binding protein 3; TC, tumor cells; TS, tumor stroma; TF, tumor front.