Fig. 4.
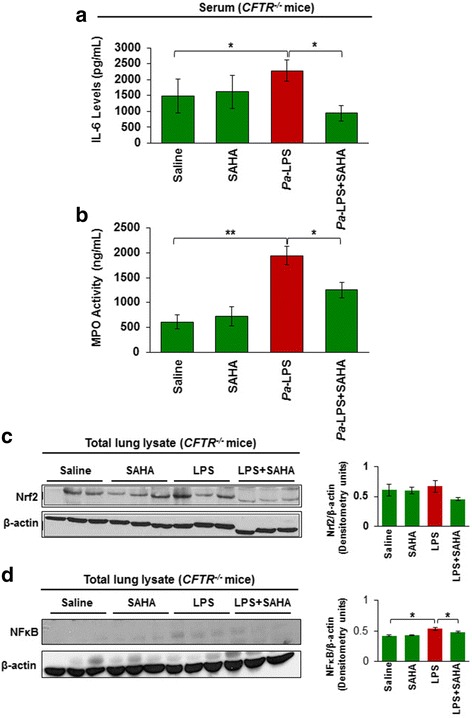
SAHA controls Pa-LPS induced inflammation and neutrophil activity in Cftr−/− mice. The age and sex matched Cftr−/− mice (n = 3, each group) were injected (i.p.) with SAHA (25 mg/kg bw) and/or Pa-LPS (15 mg/kg bw) for 36 h and serum was collected for further analysis. a IL-6 cytokine levels were quantified by sandwich ELISA. Data are shown as mean ± SEM of IL-6 levels (pg/ml). We observed that SAHA significantly inhibits (p < 0.05) Pa-LPS induced IL-6 cytokine levels. b To obtain a quantitative estimate of neutrophil recruitment and activity, a myeloperoxidase (MPO, neutrophil specific enzyme) ELISA assay was performed. We found that SAHA significantly inhibits (p < 0.05) Pa-LPS induced MPO (neutrophil activity) levels where data is shown as mean ± SD (ng/ml). c, d The age and sex matched Cftr−/− mice (n = 3, each group) were injected (i.p.) with SAHA (25 mg/kg bw) and/or Pa-LPS (15 mg/kg bw) for 36 h, and lung tissues were collected for immunoblotting. Data shows that SAHA modulates Pa-LPS induced NFκB and Nrf2 protein levels, suggesting that SAHA mediated HDACi can be developed as an effective treatment for treating chronic CF-lung disease
