Fig. 5.
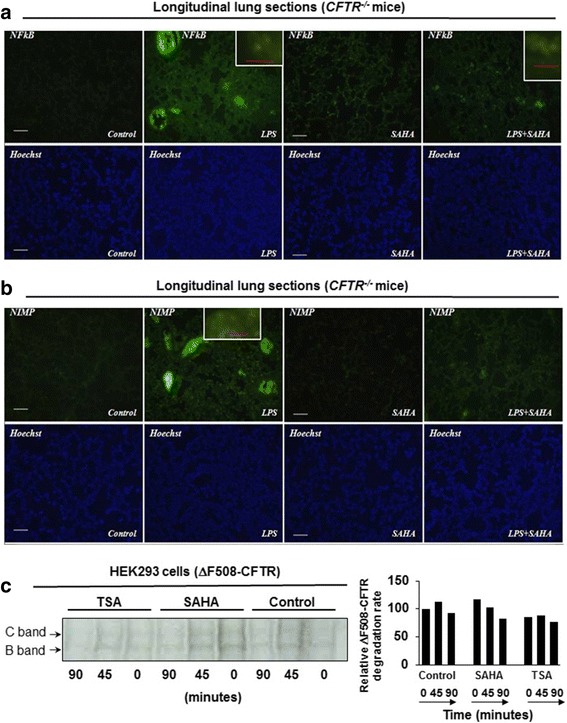
SAHA inhibits Pa-LPS induced NFκB activity and neutrophil chemotaxis. The age and sex matched Cftr−/− mice (n = 3, each group) were injected (i.p.) with SAHA (25 mg/kg bw) and/or Pa-LPS (15 mg/kg bw) for 36 h, and lung tissues were collected for immunostaining. a SAHA treated Cftr−/− mice show substantial reduction in Pa-LPS induced NFκB expression and nuclear localization in the murine lungs. b SAHA treatment also shows a substantial decline in the number of Pa-LPS driven neutrophils as depicted by NIMP R14 (a cell surface neutrophil marker) expression. Bottom panel shows the Hoechst (nuclear) staining and high-magnification images are shown in insets. Scale- 50 μM, insets-10 μM. c Next, HEK293 cells were transiently transfected with CEP-ΔF508-CFTR and treated with SAHA (10 μM) or Trichostatin A (10 μM) from 24 to 48 h. At 48 h post-transfection, cells were metabolically labelled with Trans-S35 for 30 min followed by 0, 45, and 90 min chases for evaluating the protein processing of radiolabelled CFTR by immunoprecipitation and autoradiography. The data shows that SAHA induces the expression of both the immature (B-form) and mature (C-form) forms of CFTR. Moreover, kinetic analysis suggests that SAHA slows the degradation rate of ∆F508-CFTR over untreated control and Trichostatin-A treatment. The data is representative of three independent experiments, n = 1
