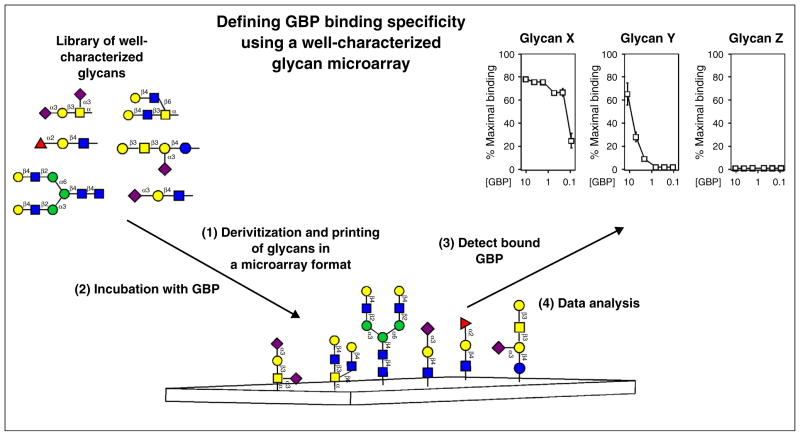
Figure 1.
Utilization of defined glycan microarrays to elucidate GBP specificity. Libraries of well-characterized glycans generated by release of defined glycans from glycoproteins, other natural sources or by chemical or chemoenzymatic synthesis are used to populate well-defined glycan microarrays. Structures reflect naturally occurring glycans and modifications of glycans not typically found in nature. Glycan libraries undergo derivatization with a functional coupling moiety, followed by printing in a microarray format to generate the glycan microarray. GBPs are incubated with the glycan microarrays over different concentrations and detected by fluorescence emission if directly labeled or by a similarly labeled suitable secondary detecting agent. While many approaches can be taken to analyze glycan array data, examination of GBP binding over a variety of concentrations for individual glycans is shown.