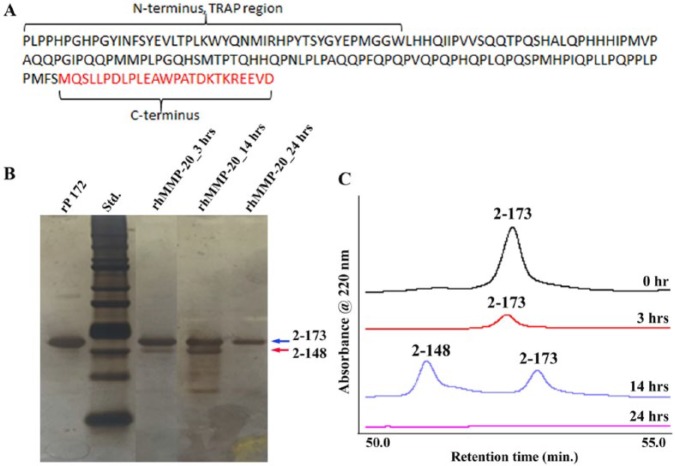
Figure 1.
Proteolysis of amelogenin rP172 by MMP-20 in the chitosan hydrogel. (A) Primary amino acid sequence of recombinant porcine amelogenin showing the 20-kDa C-terminally cleaved P148 peptide (black font) and the cleaved C-terminus (red font). The first 44 amino acids from the N-terminal region constitute the tyrosine-rich amelogenin polypeptide (TRAP) region of amelogenin. (B) Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis showing peptides obtained after proteolysis of amelogenin by rhMMP20 at 3, 14, and 24 h without chitosan hydrogel. Based on the full-length amelogenin rP172 (designated as I, amino acids 2 to 173, 25 kDa; Fig. 1A), the proteolytic products were designated as II, 2 to 148 (20 kDa), III, 46 to 148 (13 kDa; Moradian-Oldak et al. 2001; Sun et al. 2008). The major proteolytic product lacking the hydrophilic C-terminal 25 amino acids, namely, P148, appeared after 3 h of proteolysis, and its content was increased when the proteolysis time increased to 14 h. After 24 h, a full-length amelogenin band along with another band at 13 kDa persisted. The arrows represent the 20k peptide p148, and the full-length amelogenin (rp172). (C) Reverse-phase chromatography showing the amelogenin proteolysis products at various time intervals.