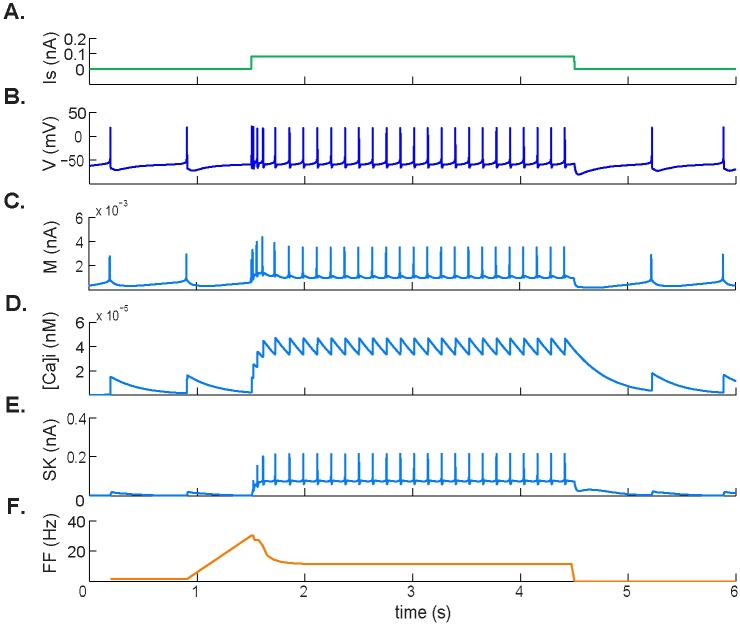
Fig 2. Spike frequency adaptation response to applied depolarizing current.
A. Applied 0.1 nA depolarizing pulse. B. Simulated membrane potential during the pulse. C. M-type potassium current dynamics showing an increase in response to initial depolarization followed by a new, elevated steady state during stimulation. D. Intracellular calcium concentration [Ca2+]i. E. Calcium-activated SK-type potassium current. [Ca2+]i and SK-type potassium current are both involved in the change in firing rate during depolarizing stimuli. F. Firing frequency.