Fig. 6. G-Rg3 Inhibits HCV-induced mitophagy.
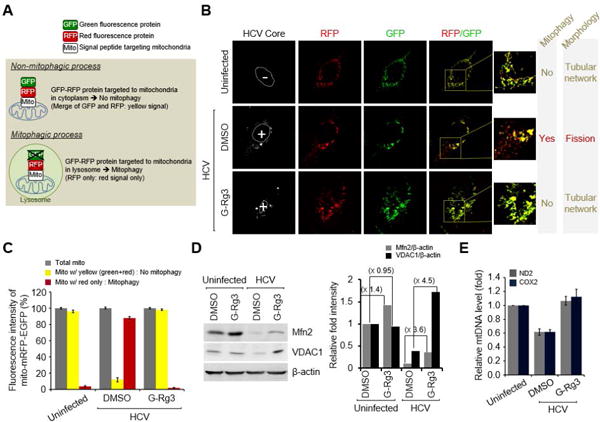
(A) A system for monitoring the mitophagosomal maturation process by which mitophagosomes are delivered to lysosomes (mitophagy) using a dual fluorescence reporter/sensor, p-mito-mRFP-EGFP. Lysosomal delivery of the tandem fusion protein mito-mRFP-EGFP targeting entire mitochondria results in differential quenching and degradation of the two individual fluorochromes, thereby allowing for visual analysis of mitophagic flux. (B) Confocal microscope images showing G-Rg3-mediated inhibition of HCV-induced mitophagy. HCV-infected cells transiently expressing mito-RFP-GFP were treated with G-Rg3 (100 μM) for 48 hours and then immunostained with anti-HCV core antibody (white). Nuclei are demarcated with white dotted circles. Infected (+) and uninfected (–) cells are marked. The fluorescence signals in the zoomed images indicate the expression of mito-RFP-GFP targeting mitochondria: yellow color, no mitophagy; red color, mitophagy. (C) Quantitative analyses of the fluorescence signals targeting mitochondria in panel A. (D) Western blot analyses of Mfn2 and VDAC1 expression in HCV-infected cells treated with G-Rg3. Whole-cell lysates extracted from HCV-infected cells treated with G-Rg3 (100 μM) for 2 days were analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies specific to Mfn2 and VDAC1 protein. β-actin was used as an internal loading control. (E) Real-time qRT-PCR analysis of mitochondrial DNA level in HCV-infected cells treated with G-Rg3. Mitochondrial ND2 and COX2 DNAs isolated from HCV-infected cells treated with G-Rg3 (100 μM) for 2 days were analyzed by real-time qRT-PCR with primers specific to ND2 and COX2 gene. β-actin was used for normalization.
