Table 2.
Substrate scope for trans-(1R,2R)-selective Mb variants.[a]
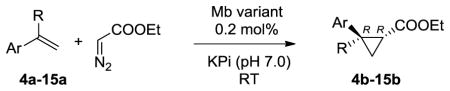
| |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| |||||
| Product | Catalyst[b] | Conv. [%] | TON | de [%] | ee [%] |
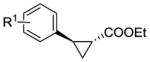
|
|||||
| R1 = 4-CH3 (4b) | RR5 | >99[c] | 165 | 96 | 63 |
| 4-MeO (5b) | RR5 | 95[c] | 160 | 97 | 74 |
| 4-Cl (6b) | RR2 | >99 | >500 | 97 | 49 |
| 4-CF3 (7b) | RR4 | 45[c] | 75 | 97 | 64 |
| 3-Me (8b) | RR4 | >99 | >500 | 92 | 84 |
| 2-Me (9b) | RR3 | >99 | >500 | >99 | >99 |
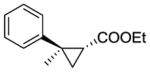 10b |
RR3 | >99[c] | 165 | 78 | 78 |
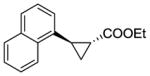 11b |
RR4 | 45[c] | 75 | 80 | 88 |
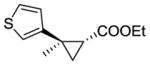 12b |
RR2 | 84 | 420 | 96 | 65 |
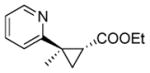 13b |
RR2 | 78 | 390 | 88 | 67 |
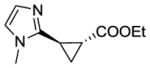 14b |
RR1 | 56[c] | 95 | 99 | 98 |
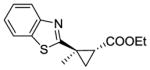 15b |
RR4 | 54[c] | 90 | 65 | 71 |
