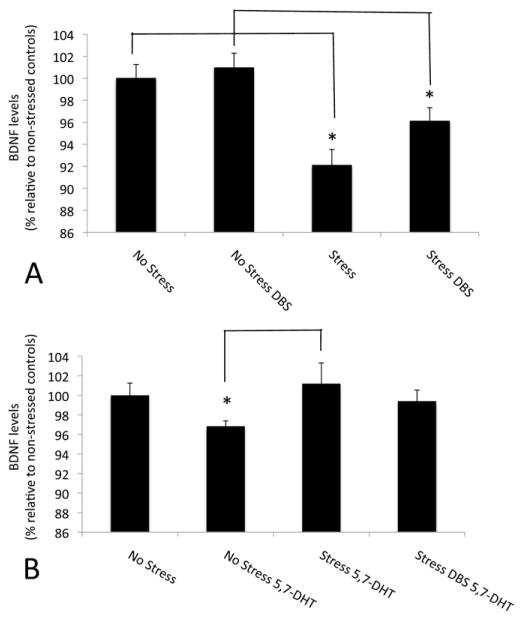
Figure 4.
Brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels in the hippocampus of animals receiving ventromedial prefrontal cortex stimulation during chronic unpredictable mild stress. (A) Hippocampal BDNF levels were significantly lower in stressed animals as compared with nonstressed control subjects (p < .0007). DBS partially reversed this deficit with a trend toward an increase in BDNF levels (p = .055). (B) In stressed animals given 5,7-DHT raphe injections, BDNF levels were higher than in corresponding serotonin-depleted control subjects (p = .02). In contrast, BDNF levels in 5,7-DHT stressed animals with or without DBS were similar to those recorded in nonstressed, nonlesioned control subjects. Values in the graph represent percentages relative to animals that did not undergo chronic unpredictable mild stress or 5,7-DHT injections. *Statistically significant. Abbreviations as in Figure 3.