Figure 2. Monozygotic (MZ) Twin Discordance in Maximum Amount Smoked Per Day by Age 17 As a Function of Discordance in ADHD and Gender.
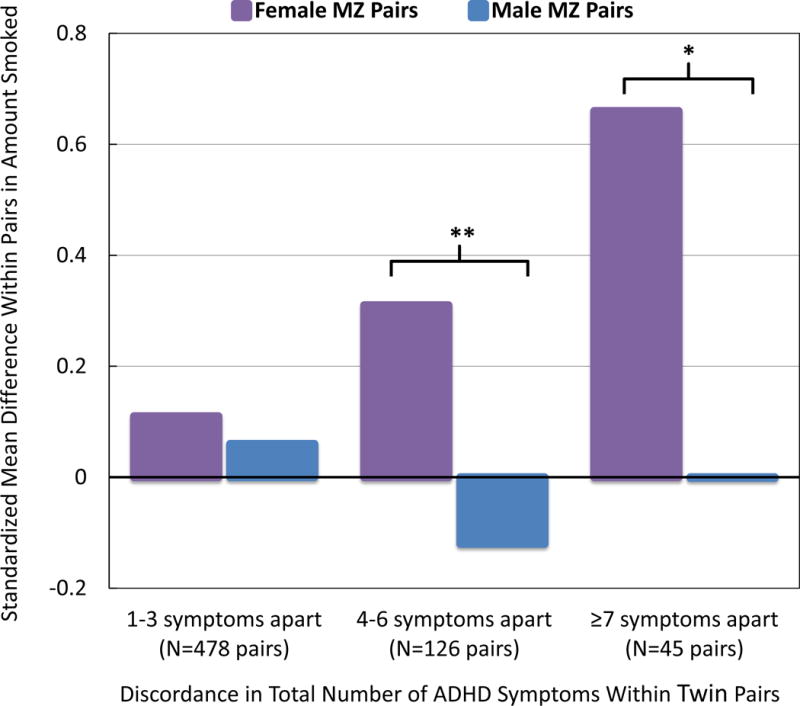
Note: MZ female twins with more ADHD symptoms than their co-twins escalated in amount smoked relative to the co-twin by age 17, reaching ~.7 SD apart in the most discordant pairs. For instance, more affected female twins smoked roughly 1/2 pack of cigarettes per day more than co-twins with 7 fewer symptoms. This effect was not evident in males. Differences between male and female MZ pairs were significant for pairs discordant by 4–6 (t = −2.79, df = 124) and ≥7 symptoms (t = −2.03, df = 43). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01
