Fig. 3.
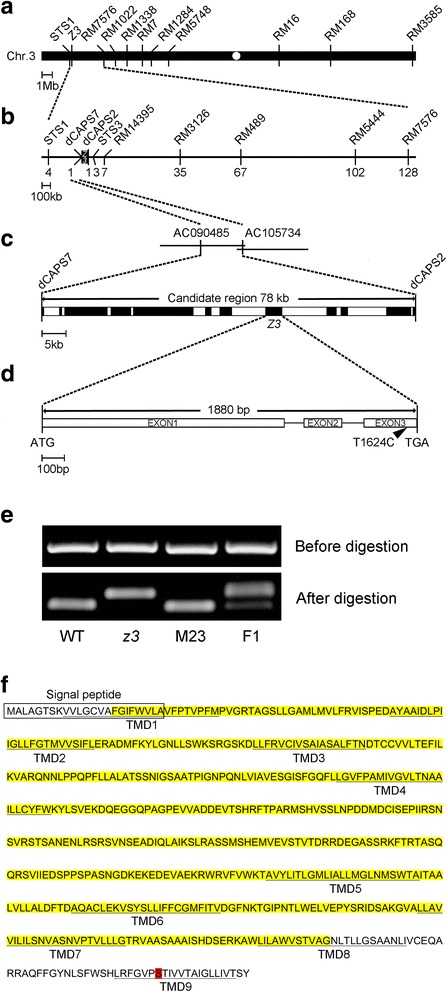
Map-based cloning of the z3 locus. a Physical mapping of the z3 locus. The z3 locus was initially mapped to a 3.91-Mb region between two markers, STS1 and RM7576, on the short arm of chromosome 3. The marker information is listed in Additional file 8: Table S1. b Fine mapping of the z3 locus. The locus was further mapped within a 78-kb region between two markers, dCAPS7 and dCAPS2. Numbers below the line indicate F2 recombinants at the marker regions. c Candidate genes (black boxes) in the 78-kb region. d T to C substitution of Z3 in the z3 mutant. Three exons and two introns are indicated as rectangles and lines, respectively. The position of the point mutation in the z3 mutant is at the third exon and represented by a black arrowhead. e Derived cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence (dCAPS) analysis of the point mutation in the z3 mutant. Aatll was able to digest the genomic PCR products amplified from the WT, but not from the z3 mutant because of its T to C substitution in the Aatll restriction enzyme site. M23, a mapping parent ‘Milyang23’; F1, F1 hybrid (z3/Milyang23). f Z3 protein sequence. The predicted N-terminal signal peptide is marked with an open rectangle and the nine transmembrane domains (TMDs) are underlined. The yellow highlight represents regions predicted to be a CitMHS family. The position of the point mutation in the z3 mutant is highlighted in red
