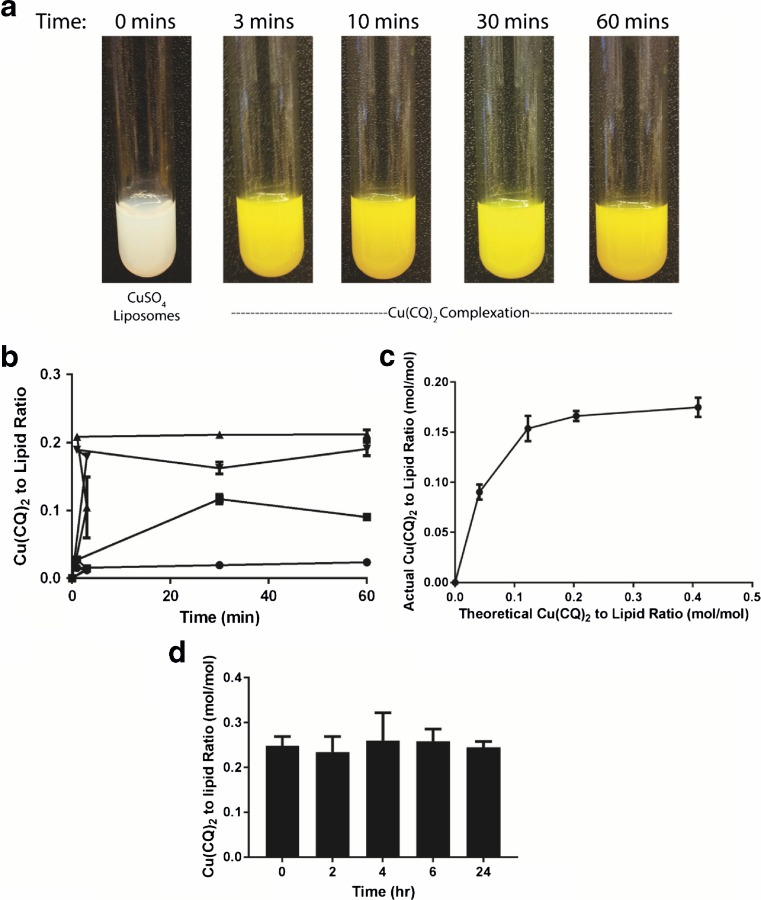
Fig. 2.
Synthesis of Cu(CQ)2 in liposomes prepared with encapsulated 300-mM CuSO4. a Photograph of solutions consisting of CQ (5 mg/mL) added to CuSO4-containing liposomes (20-mM liposomal lipid) over a 1-h time course at 40 °C. b Formation of Cu(CQ)2 inside DSPC/Chol liposomes (20 mM) as a function of time over 1 h at 4 (●), 25 (■), 40 (▲), and 60 °C (▼) following addition of CQ (5 mg/mL). c Measured Cu(CQ)2 to liposomal lipid as a function of theoretical Cu(CQ)2 to total liposomal lipid ratio estimated based on the amount of CQ added to the liposomes. For these studies, the liposomal lipid concentration was fixed at 20 mM and the added CQ amount was varied. d In vitro stability of the Cu(CQ)2 formulation over 24 h in 80% fetal bovine serum. Cu(CQ)2 was measured using a spectrophotometric assay (b–c) or HPLC (d) and liposomal lipid was measured through use of a radiolabeled lipid (3H-CHE). All data are plotted as mean ± SEM