Fig. 2.
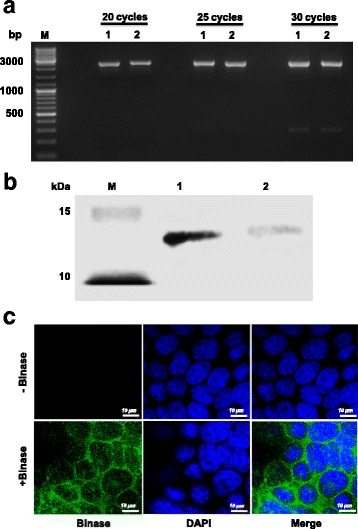
Effect of binase incubation with virus particles and MDCK-II cells. a To analyze the stability of genomic viral RNA (vRNA), virus particles were either left untreated (lane 1) or treated with binase (105 U/ml, lane 2) and incubated for 30 min at 37 °C. RT-PCR analysis of the virus particle-protected vRNA, using specific segment primers to amplify full-length PB2 segment for different number of cycles (20, 25, 30, 35), showed that binase does not affect protected H1N1pdm09 vRNA. b Internalization of binase (105 U/ml) into MDCK-II cells was detected by Western blot analysis 8 h post incubation (lane 2). After washing the binase-treated cells twice, total cell lysate was assayed. 100 ng of purified binase was used as a loading control (lane 1). M refers to protein size marker. c The internalization of binase (105 U/ml) into MDCK-II cells was further analyzed by immunostaining using rabbit polyclonal anti-binase and Alexa Fluor 488-labelled (green) chicken monoclonal anti-rabbit antibodies 4 h post incubation. Cell nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Control cells were not incubated with binase
