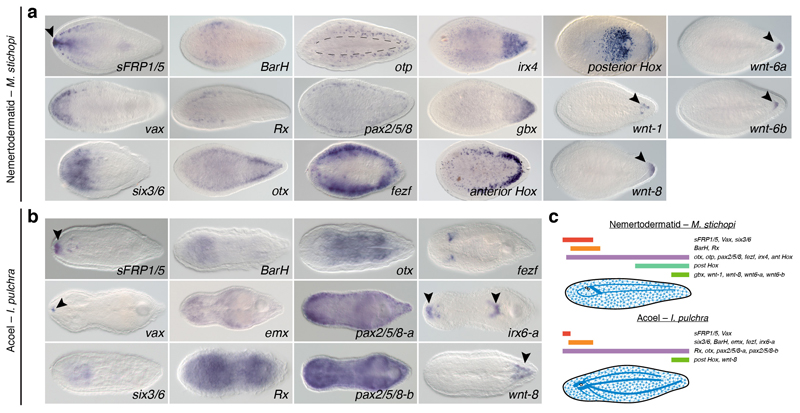
Extended Data Figure 3. Anteroposterior patterning in Xenacoelomorpha.
(a, b) Expression of anteroposterior markers in adult specimens of M. stichopi and I. pulchra. In both species, sFRP1/5, vax, six3/6, and BarH are expressed in anterior territories (black arrowheads). In M. stichopi, Rx is also expressed anteriorly, but broadly along the animal body in I. pulchra. In this acoel, emx is detected in the anterior part of the animal (background staining close to the gonads). In the nemertodermatid, the anterior neural markers otx, otp, pax2/5/8, and fezf are expressed along the entire AP axis, in association with the dorsal nerve cords (black dotted lines in otp). In I. pulchra, otx, pax2/5/8-a, and pax2/5/8-b are broadly expressed. In M. stichopi, an irx ortholog is detected in the posterior tip, while it is detected in the anterior tip and around the mouth and copulatory apparatus in the acoel (arrowheads). The gbx ortholog of M. stichopi is expressed posteriorly, and the trunk-related Hox genes are expressed in two lateral rows (anterior Hox) and anteriorly to the mouth and in the posterior tip (posterior Hox). In the nemertodermatid and the acoel, Wnt ligand genes are expressed posteriorly (arrowheads). All images are dorsoventral views with anterior to the left. (c) Schematic summary of anteroposterior expression in the nemertodermatid M. stichopi and the acoel I. pulchra. Drawings are not to scale and the extent of the expression domains are only approximate. The expression of posterior Hox in I. pulchra is based on23.