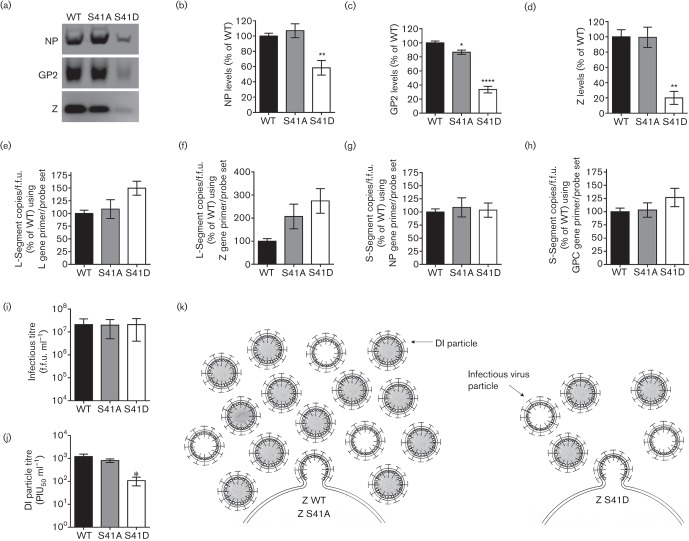
Fig. 3.
The S41 phosphomotif regulates DI particle production. (a–h) Comparison of viral structural protein and genome content in preparations of rLCMV WT, S41A or S41D virus. Vero E6 cells were infected with WT or S41-mutant rLCMV at a MOI of 0.0001 and clarified supernatants were collected 72 h later. Equivalent f.f.u.s of each rLCMV were then concentrated through a 20 % sucrose cushion by ultracentrifugation. Viral protein content in these concentrated virus preparations was analysed by quantitative Western blotting. Representative Western blots (a) as well as the quantity (mean±sem) of NP (b), GP (c) or Z (d) contained in each rLCMV virus preparation are shown. The copies of LCMV genomic L-segment (e–f) or S-segment (g–h) were determined by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) (Haist et al., 2015) and then normalized to the infectious titre (f.f.u.). To enumerate copies of L-segment vRNA, RT was performed using the RT primer 5906−, followed by qPCR using the primer probe sets located in either the L gene (primers L5517+ and L5645− and probe L5582−P) (e) or Z gene (primers L212+ and L276− and probe L251−P) (f). To determine the copies of S-segment vRNA, RT was performed using the RT primer 2865−, followed by qPCR using the primer probe sets located in either the NP gene (primers S2275+ and S2338− and probe S2295+P) (g) or GPC gene (primers S929+ and S988− and probe S952+P) (h). (i–j) Measurement of standard infectious virus and DI particles produced by rLCMV WT, S41A or S41D. The infectious titre of each of the clarified supernatants used in (a–h) was determined by focus forming assay (i) and the DI particle titre was assessed by plaque interference assay (j). PIU50 ml−1, plaque interfering units50 ml−1. For (b–j), values represent the mean±sem of protein (b–d), viral genome (e–h), f.f.u. ml−1 (i) or DI particle titre (j) from four independent experiments and statistical analyses were performed by one-way ANOVA with Holm–Sidak’s test for multiple comparisons for which *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ****, P<0.0001. (k) Model of S41’s impact on infectious virus and DI particle formation. WT virus containing the native S41 (Z WT) produces high levels of infectious and DI particles. Mutation of S41 to alanine (Z S41A) to prevent phosphorylation has little effect on infectious or DI particle production. Mutation of S41 to aspartic acid (Z S41D) to mimic the negative charge associated with phosphorylation of S41 results in decreased infectious virus and DI particle release. The S41D mutation disproportionately impacts DI formation over standard infectious virus.