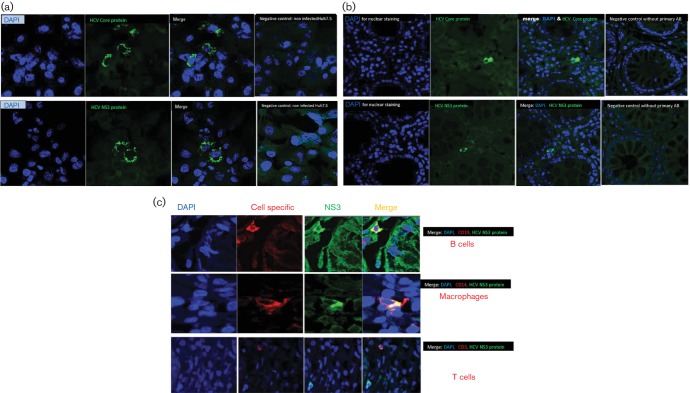
Fig. 1.
(a) Confirmation of the specificity of the immunohistochemistry of HCV core and NS3 antigens using Huh7.5 cell lines. The specificity of the immunohistochemical staining of HCV antigens was confirmed on Huh7.5JFH1 cell line infected with HCV and uninfected Huh7.5 cell line using primary mouse monoclonal antibodies against HCV core and NS3 proteins. The cells expressing HCV antigens were identified by the specific green cytoplasmic signals (Alexa Fluor® 488 Donkey Anti-Mouse secondary antibody). No positive staining was observed in HCV-uninfected Huh7.5 cell line. (b) Immunohistochemical detection of extra-hepatic infection of HCV in colonic tissue of HCV-infected patients: HCV core protein and NS3 as markers of HCV replication were detected by indirect fluorescent immunohistochemical staining and confocal imaging using mouse monoclonal anti-core antibody and mouse monoclonal anti-HCV NS3 antibody. Positive cells were identified by the green cytoplasmic signals (by Alexa Fluor® 488 Donkey Anti-Mouse secondary antibody). No positive signals were detected in the negative control without primary antibodies. (c) Identification of the cell types in colonic tissue with extra-hepatic HCV infection. To examine cell types where HCV infects extra-hepatically, double immunofluorescence staining on the colonic tissue was performed. Colonic tissue sections were stained with mouse monoclonal anti-HCV NS3, as a marker of HCV infection, and antibody against a specific cell marker (for T cells [anti-CD3], for B [anti-CD19] lymphocytes and for macrophage/monocytes [anti-CD14]). The cells in which HCV infects were identified by co-expression of NS3 and the cell-specific marker. HCV NS3 was expressed in B cells and macrophage but not in T cells.