Fig. 6. E4B and CHIP-dependent ubiquitination of substrate proteins in HEK293 cells.
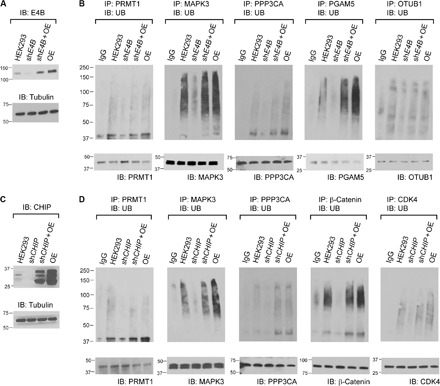
(A) Inhibition of E4B expression in HEK293 cells by shE4B was confirmed by Western blotting probed with an antibody against E4B. (B) Ubiquitination of PRMT1, MAPK3, PPP3CA, PGAM5, and OTUB1 in HEK293 cells was assayed by immunoprecipitation with antibodies against each substrate proteins and probing their ubiquitination levels with an anti-UB antibody on the Western blots. The cells were treated with 10 μM MG132 for 1.5 hours before they were lysed. The ubiquitination of each substrate protein was compared among the control HEK293 cell (HEK293), HEK293 expressing shE4B (shE4B), HEK293 expressing both shE4B and recombinant E4B complementary DNA (cDNA) (shE4B + OE), and HEK293 overexpressing E4B from recombinant cDNA (OE). IgG, immunoglobulin G. (C) Similar to (A) to confirm the inhibition of CHIP expression in HEK293 cells by shCHIP. (D) Similar to (B) to confirm CHIP-dependent ubiquitination of PRMT1, MAPK3, PPP3CA, β-catenin, and CDK4 in HEK293 cell (HEK293) and its derivatives expressing shCHIP (shCHIP), shCHIP and recombinant CHIP (shCHIP + OE), and recombinant CHIP (OE).
