Figure 1.
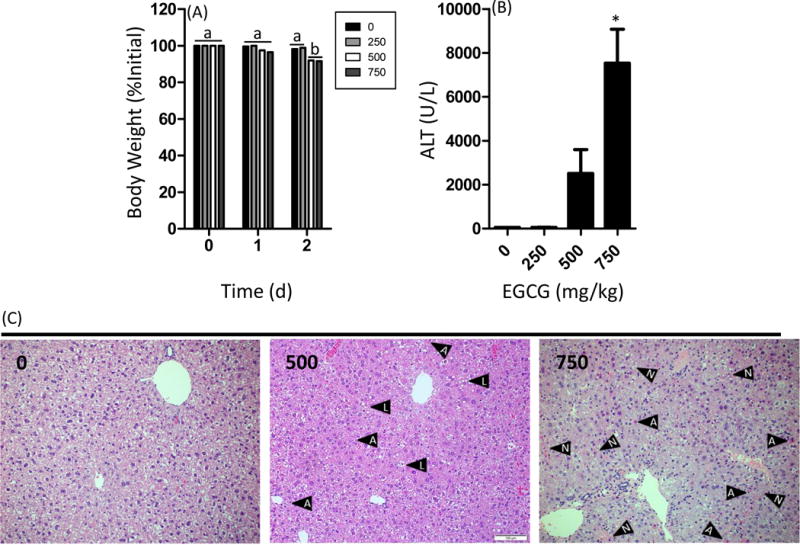
Impact of oral bolus EGCG on body weight gain and plasma alanine aminotransferase levels in C57BL/6J mice. Mice were fasted for 7 h and then treated once daily with EGCG by oral gavage for three days. (A) Mice were weighed daily. Mice were euthanized 1 h after the third dose. (B) Plasma ALT levels were determined using a commercially-available spectrophotometric assay. (C) Histopathological analysis was performed to determine the extent of EGCG-induced hepatotoxicity. Data represent the mean ± SEM for n = 10–18. Body weight changes were compared using two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test. Different superscript letters indicates p < 0.05 between treatment groups. ALT levels were compared using one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-test. An asterisk indicates p < 0.05 compared to control mice. Histologpathological images shown are representative images. Black arrows containing an “A” indicates an apoptotic body, those with an “L” indicate lipid droplets, and those with an “N” indicate areas of necrosis.
