Figure 2.
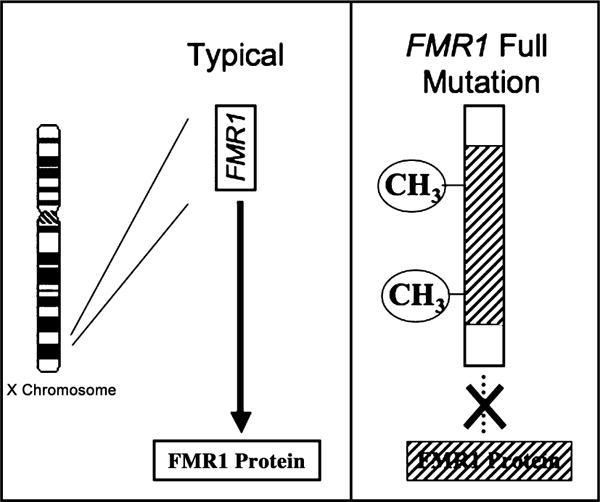
The genetic basis for the fragile X full mutation. FMR1 gene from X chromosome shown on left under typical conditions. Modal trinucleotide (CGG) repeat length is 29–30. Significantly expanded CGG repeats in the FMR1 full mutation (right) lead to hypermethylation (CH3), transcriptional repression and reduced levels of FMRP. Reduced levels of FMRP lead to neurobiological dysfunction and the cognitive-behavioral phenotype (also see Figure 3)
