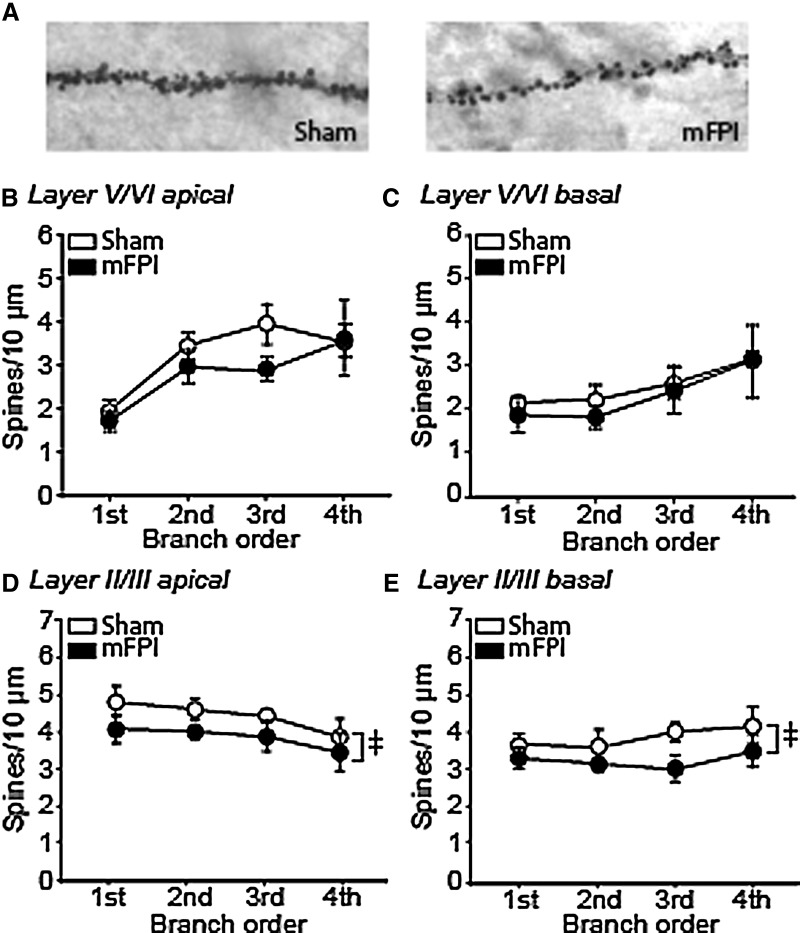
FIG. 5.
Lateral mFPI significantly reduces overall spine density in layer II/III pyramidal neurons of the IL. (A) Representative images of third-order apical dendrites and spines from a sham and an mFPI animal. Summary data showing of the number of spines/10 μm counted in first- to fourth-order (B) apical and (C) basal dendrites from layer V/VI pyramidal neurons from sham and mFPI rats. (D) Summary data showing that mFPI causes a significant overall, but not on individual branch orders, decrease in spine density (spines/10 μm) on apical dendrites from layer II/III pyramidal neurons compared to sham animals. (E) Significant decreases in overall (but not on individual branch orders) spine density (spines/10 μm) on basal dendrites from layer II/III pyramidal neurons were observed in mFPI animals compared to sham controls. Data are mean ± standard error of the mean. ‡Significant difference between sham and mFPI by two-way analysis of variance. mFPI, mild fluid percussion injury.