-
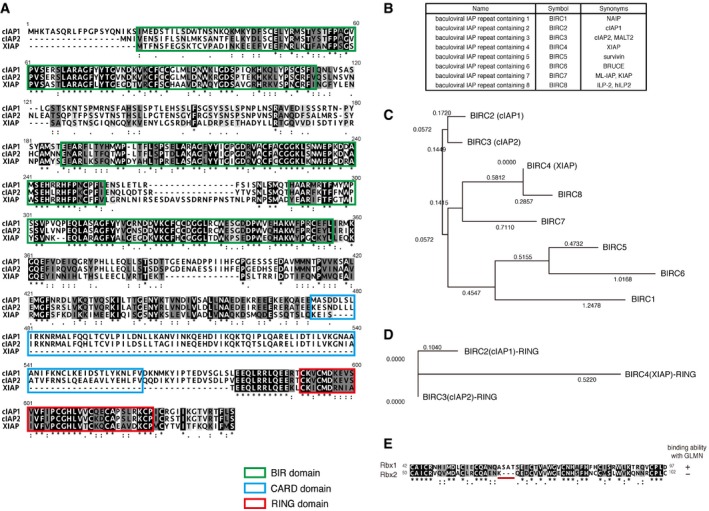
A
Comparison of amino acid sequences of cIAP, cIAP2, and XIAP, aligned using ClustalW. Green, blue, and red boxes indicate the BIRs, CARD, and RING, respectively. The three BIRs and RING are highly conserved among all three proteins. XIAP lacks the CARD, which is well conserved between cIAP1 and cIAP2.
-
B
A list of the BIRC family members. The human BIRC family consists of eight members. A common feature of all BIRCs is the presence of BIR domain(s) in one to three copies. BIRC2 (cIAP1), BIRC3 (cIAP2), BIRC4 (XIAP), BIRC7, and BIRC8 possess RING zinc‐finger domains that can act as E3 ligases.
-
C, D
Phylogenetic analysis of BIRC family members. The neighbor‐joining (NJ) method was used to create a phylogenetic tree using the Genetyx‐Mac software. The amino acid sequences of full‐length of BIRC family members (C) or RING domains (D) were analyzed. The phylogenetic tree shows that cIAP1 and cIAP2 are closely related to each other, whereas XIAP is located on another branch.
-
E
Amino acid sequence alignment of the RING domains of Rbx1 and Rbx2. Identical amino acids (black) and similar amino acids (gray) are shaded. The RING domain is highly conserved between Rbx1 and Rbx2, except for the motif underlined in red.