Figure 4.
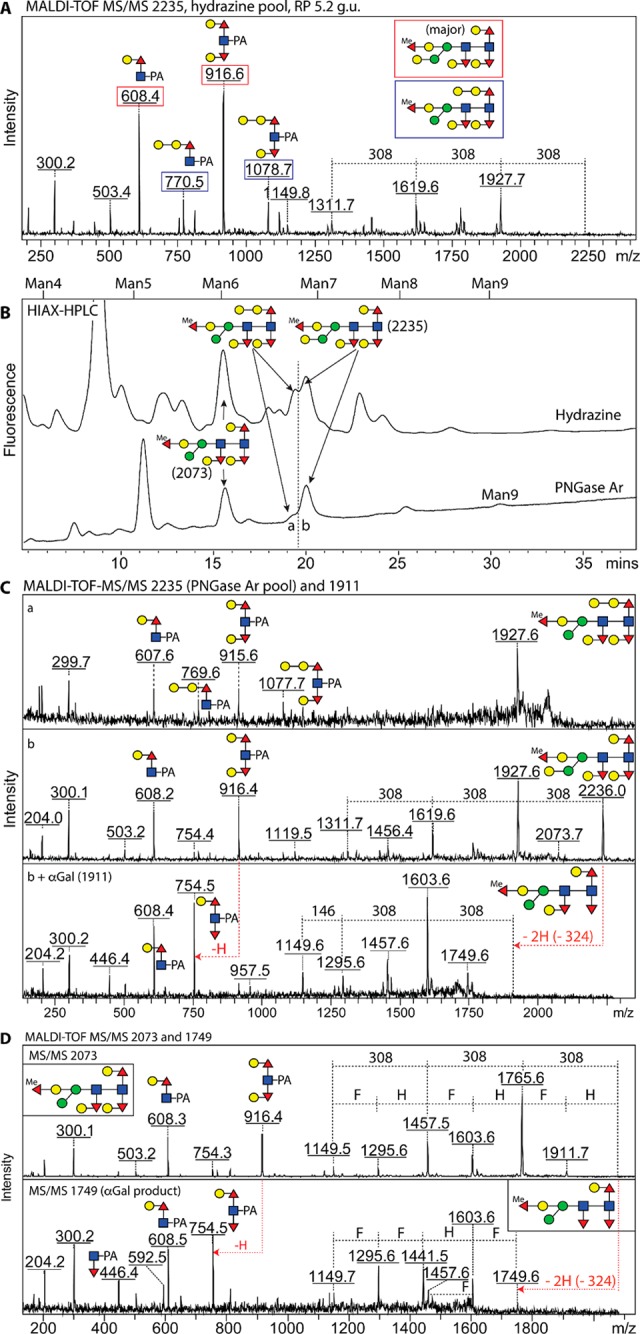
HIAX-HPLC separation of Hex6–7HexNAc2Fuc4Me1 glycans released with hydrazine or PNGase Ar from wild-type C. elegans glycopeptides. (A) The MS/MS spectrum of m/z 2235 in the 5.2 g.u. RP-HPLC fraction displayed two sets of Y-fragment ions of m/z 608/916 and m/z 770/1078, suggestive of cofragmentation of two coeluting isomers. (B) The isomers were separated by applying the 5.2 g.u. fractions to a HIAX column externally calibrated with a mixture of oligomannosidic structures (Man4–9GlcNAc2). (C) MS/MS spectra of the m/z 2235 structures in the HIAX fractions (a and b) confirmed that PNGase Ar released the same forms of Hex7HexNAc2Fuc4Me1 as hydrazine, whereby the m/z 916 fragment of the later-eluting isomer is replaced by one at m/z 754 after α-galactosidase treatment; for other structural analyses and digests on these glycans, see Supplementary Figure 6. (D) 2D-HPLC also purified an m/z 2073 Hex6HexNAc2Fuc4Me1 glycan with a fully modified core with three Gal–Fuc subunits as shown by its MS/MS pattern; the galactose caps on the proximal and distal α1,3-linked fucose residues were sensitive to α-galactosidase resulting in a final product of m/z 1749 after extended incubation.
