Figure 5.
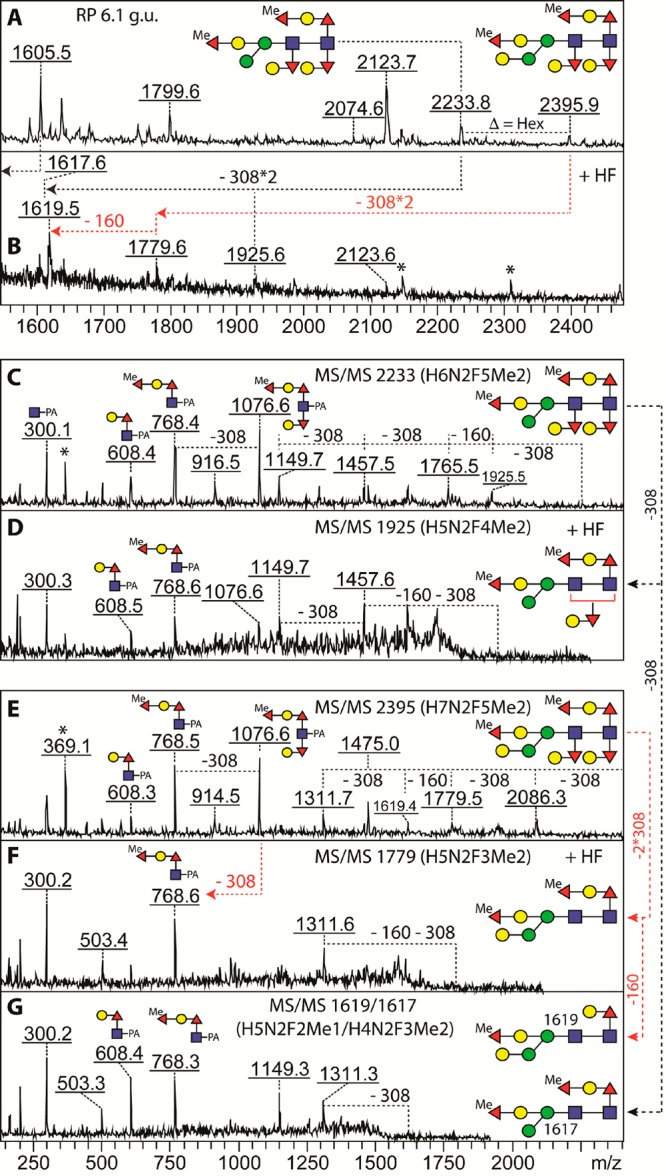
Maximal degree of fucosylation in wild-type C. elegans N-glycans. (A) The 6.1 g.u. fraction contained glycans of Hex6–7HexNAc2Fuc5Me2 (m/z 2233 and 2395) which both displayed a novel MS/MS fragment at m/z 1076 (Hex2GlcNAc1Fuc3Me1–PA; C and E) in addition to one at m/z 768 (Hex1HexNAc1Fuc2Me1–PA). (B) HF treatment resulted in sequential loss of two GalFuc units (308 Da) and, in the case of the m/z 2395 glycan, also a methylfucose (160 Da), leading to products with m/z 1925, 1779, and 1617/1619 whose MS/MS indicated loss of the m/z 1076 fragment (D, F–G). The two HF products at m/z 1617 (from m/z 2233, black-dashed arrows) and 1619 (from m/z 2395, red dashed arrows) were cofragmented, displaying two diagnostic ions (m/z 608 and 768) with equal intensities; the methylated fucose at the bisecting position was more resistant to HF treatment than the one on the core Galβ1,4Fucα1,6 motif. Asterisks in part B indicate non-glycan contaminants, whereas those in parts C and E indicate a PC-containing fragment (m/z 369; PC–HexNAc) originating from coeluting glycans.
