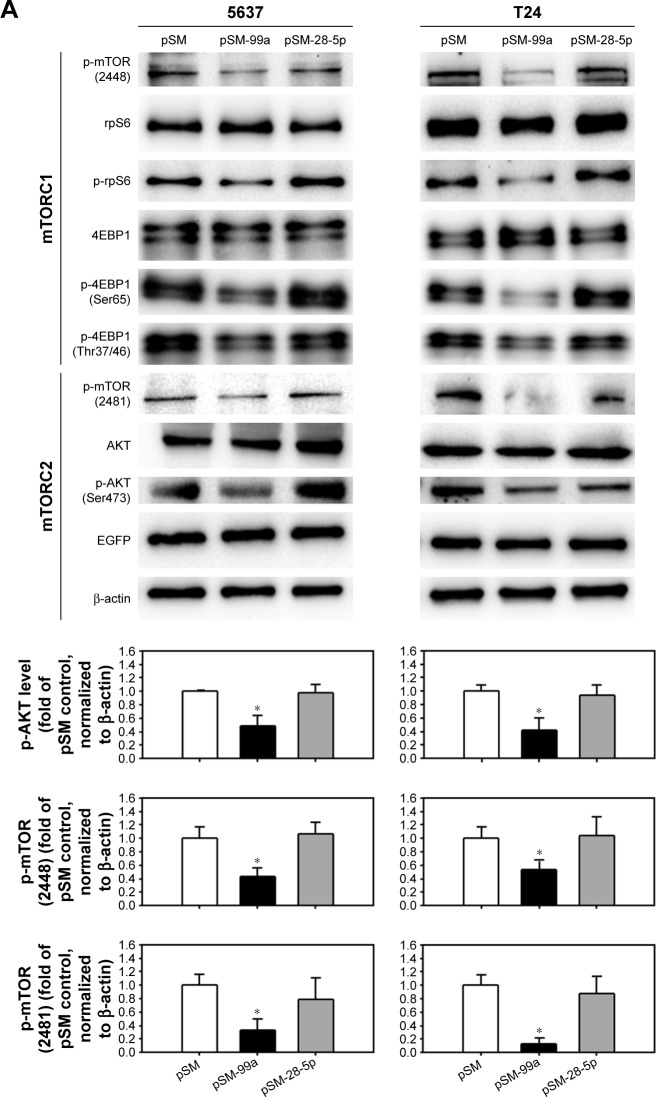
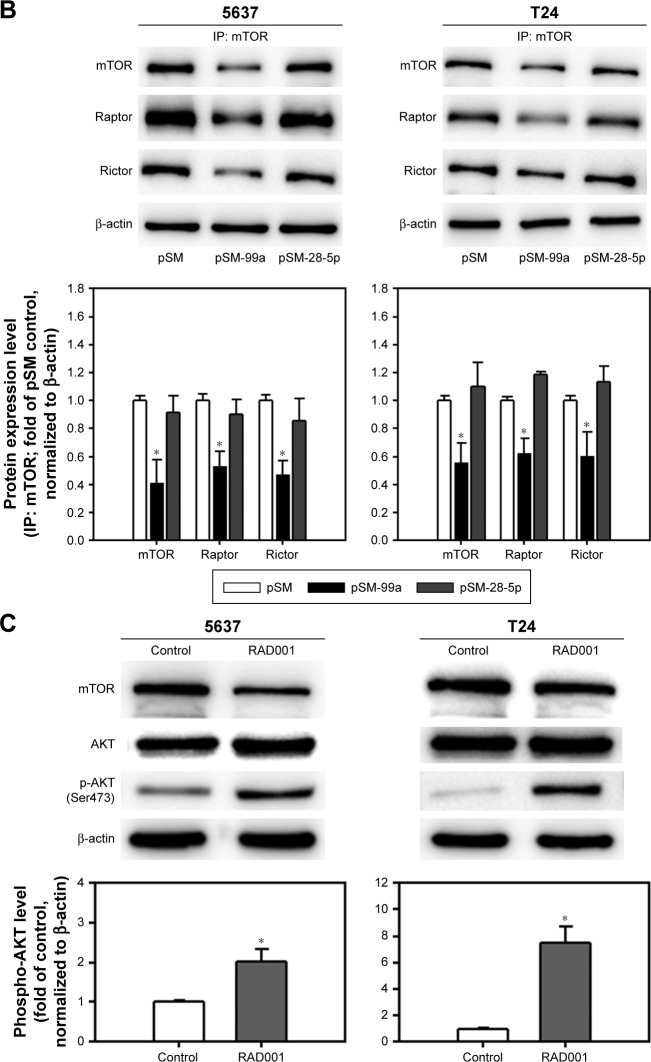
Figure 6.
Dual inhibition of mTORC1 and mTORC2 in miR-99a-5p-expressing cells compared to RAD001-treated cells.
Notes: (A) The expression level of phospho-mTOR (Ser2448), rpS6, phospho-rpS6, 4EBP1, phospho-4EBP1 (Ser65), phospho-4EBP1 (Thr37/46), phospho-mTOR (Ser2481), total AKT and phospho-AKT (Ser473) was detected in cells transfected with pSM, pSM-99a or pSM-28-5p. EGFP, which co-expressed with miRNA transcripts in the pSM vector, was detected, and β-actin was used as a loading control. The expression level of phospho-AKT in each treatment was quantified as shown in the lower panel. (B) The protein lysates from cells transfected with pSM, pSM-99a or pSM-28-5p were subjected to IP with anti-mTOR antibody overnight, and then, mTOR immunoprecipitates (IP: mTOR) were subjected to Western blot analysis for mTOR, Raptor and Rictor. (C) The expression level of phospho-AKT (Ser473) in 24 h control (dimethyl sulfoxide[DMSO])-treated) or RAD001-treated cells was determined by Western blot. The expression of β-actin served as a loading control. The relative protein levels in each treatment were quantified as shown in the lower panel. *P<0.05.
Abbreviations: mTORC1, mTOR complex 1; mTORC2, mTOR complex 2; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; EGFP, enhanced green fluorescent protein; IP, immunoprecipitation.