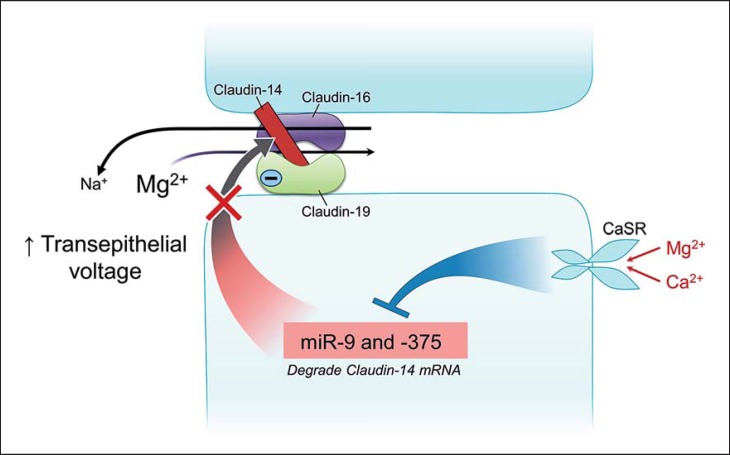
Fig. 3.
Regulated paracellular Mg2+ absorption in the thick ascending limb of Henle (TAL). Claudin-16 by itself is highly permeable to Na+, and claudin-19 is impermeable to Cl−. Claudin-14 deters the sodium channel permeability of claudin-16. Na+ backleaks into the distal part of the TAL and helps in maintaining a positive luminal voltage. Blockage of this action of claudin-14 compromises the positive luminal voltage and diminishes the driving force for Mg2+ absorption. The deterrence of Cl− passage by claudin-19 creates a negative microdomain charge, creating a selective attraction to luminal Mg2+ and Ca2+. The basolateral calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR), when activated by an elevated concentration of Mg2+ or Ca2+, inhibits miR-9 and miR-375. The inhibition removes the interference of the microRNAs with claudin-14 translation, resulting in an increased claudin-14 translation and claudin-14-mediated inhibition of claudin-16, thus inhibiting Mg2+ and Ca2+ absorption.