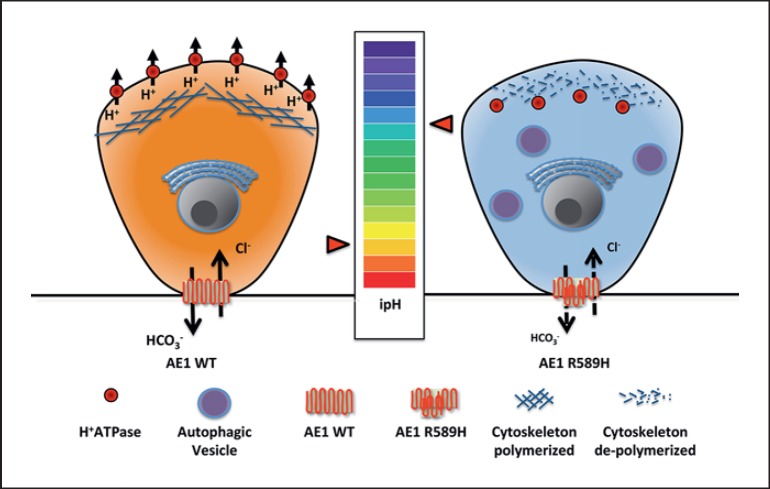
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of the novel identified mechanisms of diseases caused by R589H AE1 mutation. On the left, a normal A-IC is represented, while on the right, an A-IC expressing the R589H AE1 mutation is shown. We hypothesized that reduced expression of R589H AE1 leads to alkalinization of intracellular pH because of intracellular bicarbonate retention. This leads to actin cytoskeleton depolymerization and thus to intracellular retention of vH+ATPase.