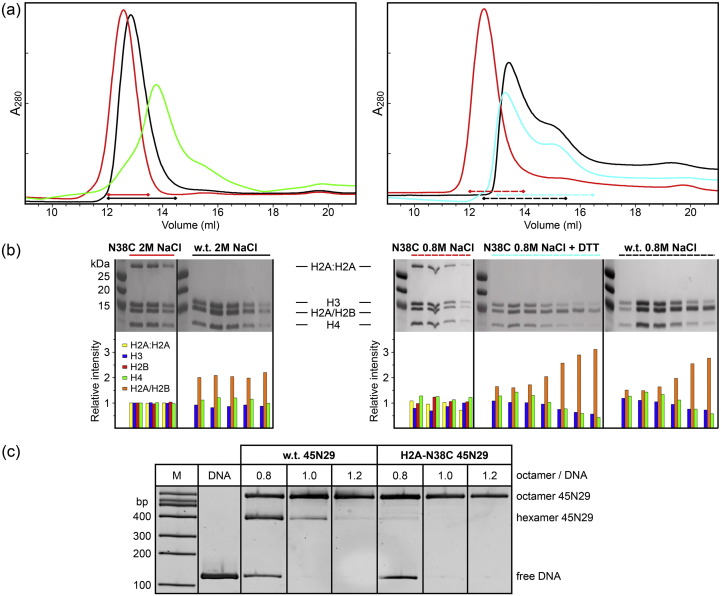
Fig. 2.
Characterization of histone octamer and a nucleosome containing H2A-N38C. (a) Size exclusion on Superdex 200. The left panel shows chromatography in 2 M NaCl for oxidized H2A-N38C octamer (red) and w.t. octamer (black) at pH 7.5, and for oxidized H2A-N38C at pH 5.0 (green). The right panel shows chromatography in 0.8 M NaCl for w.t. octamer (black), oxidized H2A-N38C octamer (red) and reduced H2A-N38C octamer (cyan) at pH 7.5. (b) SDS PAGE of peak fractions from panel a. Each upper panel corresponds to a series of fractions from a peak underlined in panel a for H2A-N38C-containing or w.t. histone octamer. The bottom panels show the amount of each core histone relative to the amounts in the H2A-N38C 2 M NaCl panel as estimated by gel densitometry. The H2A-N38C disulfide of the H2A:H2A dimer is reduced on the addition of DTT (panel N38C 0.8 M NaCl versus N38C 0.8 M NaCl + DTT). Marker proteins are shown in the left lanes. (c) Native PAGE analysis of nucleosome 45N29 containing w.t. and N38C octamers. The octamer to DNA ratio used for each assembly reaction is indicated. Marker DNAs are shown in the left lane (M).