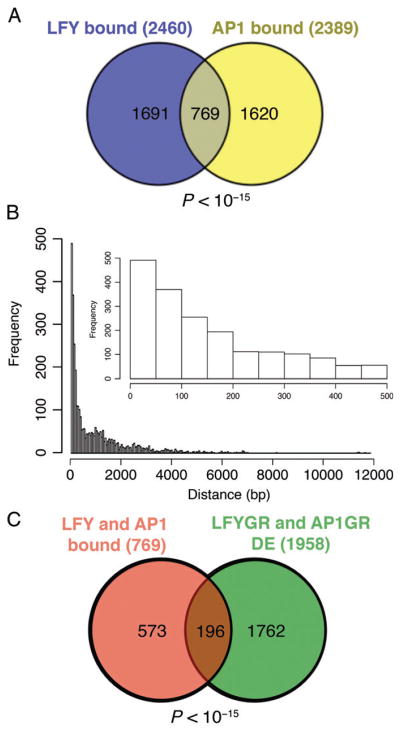
Fig. 1.
Identification of direct LFY and AP1 target genes. (A) Genes directly bound by either LFY (Moyroud et al. 2011, Winter et al. 2011) or AP1 (Kaufmann et al. 2010, Pajoro et al. 2014) or by both transcription factors. While LFY and AP1 have unique target genes, there is a significant subset of genes (769 genes; P-value < 10−15, χ2 test) whose regulatory regions are bound by both LFY and AP1. (B) Distance between AP1 peak summits and the nearest LFY-binding peak summit in the genes bound by both transcription factors. Inset: Close-up showing AP1-binding sites 500 bp or less away from LFY-binding sites. (C) Of the 769 genes bound by LFY and AP1, a significant subset (196 genes; P-value < 10−15, χ2 test) was differentially expressed (FDR < 0.01) in both LFY-GR and AP1-GR plants on the basis of public transcriptome data (Kaufmann et al. 2010, Winter et al. 2011, Pajoro et al. 2014).