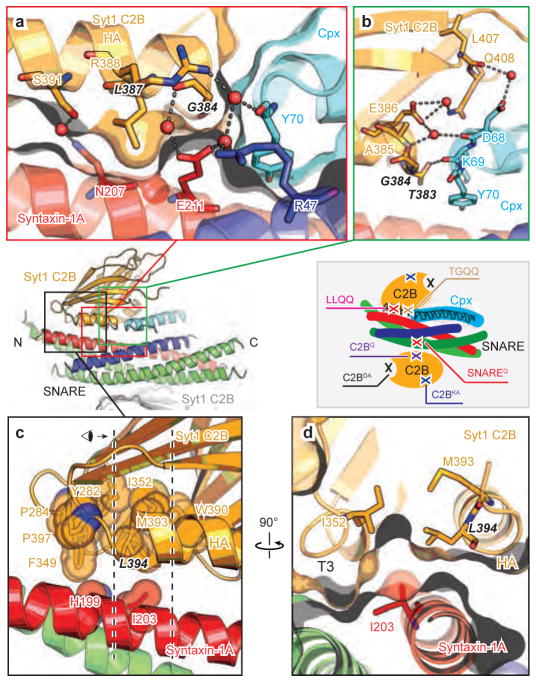
Figure 2. Close-up views of the SNARE-Cpx-Syt1 tripartite interface.
a–d, Interacting residues are shown in stick representation and labelled, water molecules are shown as red balls, hydrogen bonds and salt bridges are shown as dashed lines. Molecular surfaces are shown in panels a and d. a, interactions between the α-helix HA of the Syt1 C2B domain and syntaxin-1A. Leu387 in Syt1 C2B protrudes into the cavity of syntaxin-1A and Ser391 in Syt1 C2B forms a water-mediated hydrogen bond with Gln207 in syntaxin-1A. b, Close-up view of the interactions between the N-terminal end of the α-helix HA of the Syt1 C2B domain and the C-terminal end of the Cpx central α-helix. The main chain carboxyl of Asp68 in Cpx forms hydrogen bonds with the main chain of Glu386 in the Syt1 C2B domain and is involved in water-mediated hydrogen bonds with the side chain of the same residue. The main chain carboxyl of Lys69 in Cpx interacts with side chain Oγ of Thr383 in the Syt1 C2B domain, while the main chain of Gly384 in Syt1 C2B domain is involved in water-mediated hydrogen bonds with the side chain of Glu211 in syntaxin-1A. c and d, Close-up views of a region of hydrophobic interactions involved in the tripartite interface. Hydrophobic residues are shown in sphere representation. Dashed lines in panel c indicate the depth of the section shown in panel d. Inset, schema showing the approximate locations of the mutations.