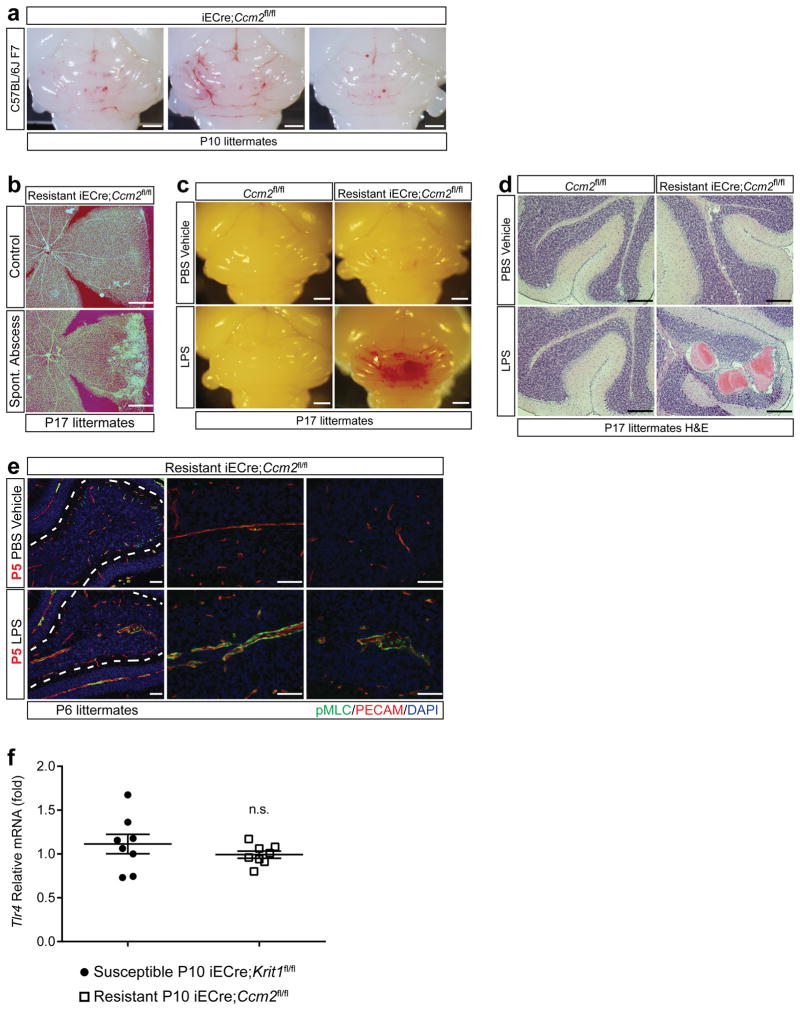
Extended Data Figure 1. CCM formation in resistant iECre;Ccm2fl/fl animals is stimulated by abscess formation and LPS.
a, Resistance to CCM formation is maintained in a C57BL/6J strain background. iECre;Ccm2fl/fl animals were back-crossed 7 generations onto a C57BL/6J background and gene deletion induced at P1 with visual hindbrain assessment at P10. N=7. Scale bars, 1 mm. b, Retinal CCM formation is stimulated by gram negative bacterial infection. Retinas of P17 resistant iECre;Ccm2fl/fl littermates are shown. The sample shown below is from the animal that developed the spontaneous gram negative abscess shown in Fig. 1c. Scale bars, 500 μm. c–d, Administration of LPS does not drive CCM formation in Cre-negative neonatal mice. LPS was administered intravenously to Ccm2fl/fl and iECre;Ccm2fl/fl littermates as shown in Figure 1g, and hindbrains assessed at P17 visually (c) and histologically (H&E staining, d). N≥3 per group. Scale bars, 1 mm (c) and 100 μm (d). e, LPS induces myosin light chain activation in CCM-deficient brain endothelial cells. Phospho-myosin light chain (pMLC) and PECAM staining of hindbrains from P5 LPS- or vehicle-injected resistant iECre;Ccm2fl/fl littermates. Dotted lines trace the purkinje cell layer. N≥4 per group. Scale bars, 50 μm. f, Tlr4 expression does not differ between CCM susceptible and resistant animals. Tlr4 expression was measured using qPCR in cerebellar endothelial cells isolated from the indicated animals at P10. Error bars shown as s.e.m. and significance determined by unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t-test. n.s. indicates p>0.05.