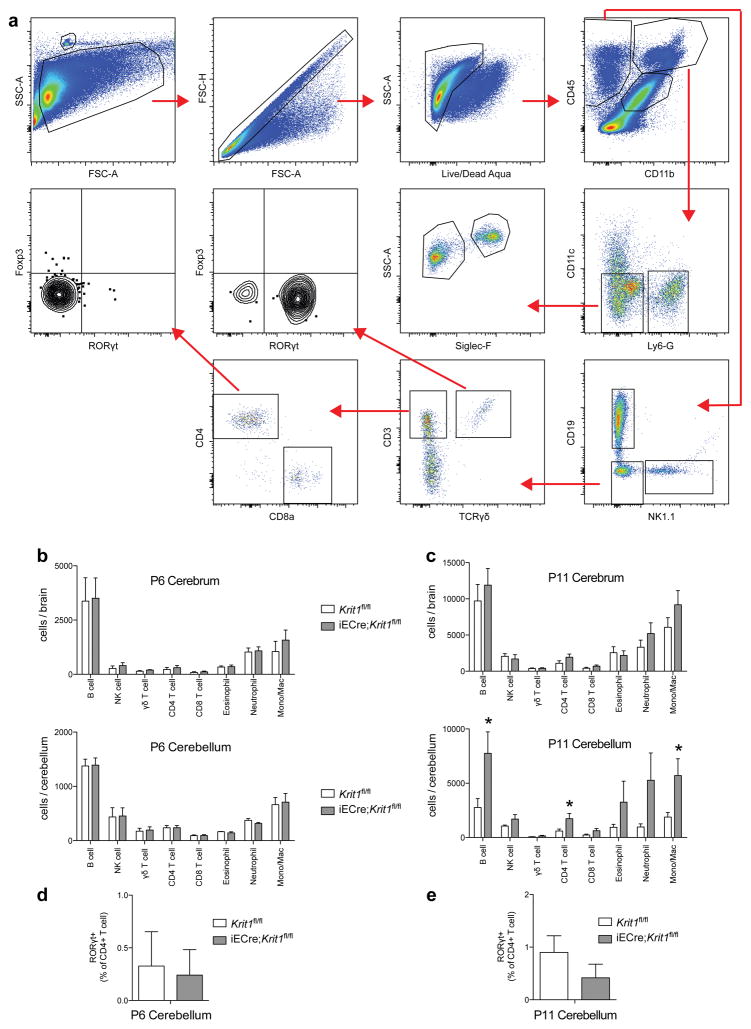
Extended Data Figure 2. Analysis of immune cells in P6 and P11 Krit1fl/fl and iECre;Krit1fl/fl brains.
a, Gating strategy for B cells, NK cells, γδ T cells, CD4 T cells, CD8 T cells, eosinophils, neutrophils and monocytes/macrophages from cerebrum and cerebellum is shown. Cellular surface markers used were as follows: Neutrophils (CD45+, CD11b+, Ly6-G+), Eosinophils (CD45+, CD11b+, CD11c−, Ly6G−, Siglec-F+, SSChi), Monocyte/Macrophage (CD45+, CD11b+, CD11c−, Ly6G−, Siglec-F−, SSClo), NK cells (CD45+, CD11b−, CD19−, NK1.1+), B cells (CD45+, CD11b−, NK1.1−, CD19+), γδ T cell (CD45+, CD11b−, NK1.1−, CD19−, CD3+, TCRγδ+), CD4 T cell (CD45+, CD11b−, NK1.1−, CD19−, CD3+, TCRγδ−, CD8−, CD4+), CD8 T cell (CD45+, CD11b−, NK1.1−, CD19−, CD3+, TCRγδ−, CD4−, CD8+). b, The number of B cells, NK cells, γδ T cells, CD4 T cells, CD8 T cells, eosinophils, neutrophils, and monocytes/macrophages isolated from P6 cerebrum (top) and cerebellum (bottom) is shown for susceptible Krit1fl/fl and iECre;Krit1fl/fl littermates. N≥6 per group. No significant differences were detected. c, The number of B cells, NK cells, γδ T cells, CD4 T cells, CD8 T cells, eosinophils, neutrophils, and monocytes/macrophages isolated from P11 cerebrum (top) and cerebellum (bottom) is shown for susceptible Krit1fl/fl and iECre;Krit1fl/fl littermates. N≥6 per group. d–e, Frequency of RORγt+ CD4 T cells isolated from P6 and P11 cerebellum. N≥6 per group. Error bars of all graphs shown as s.e.m. and significance determined by unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t-test. *indicates p<0.05. Note that there is significant immune cell presence in the cerebellum of susceptible iECre;Krit1fl/fl animals at P11 but not at P6.