Figure 1. Labeling of RGCs and Retinal Axons with Brainbow AAVs.
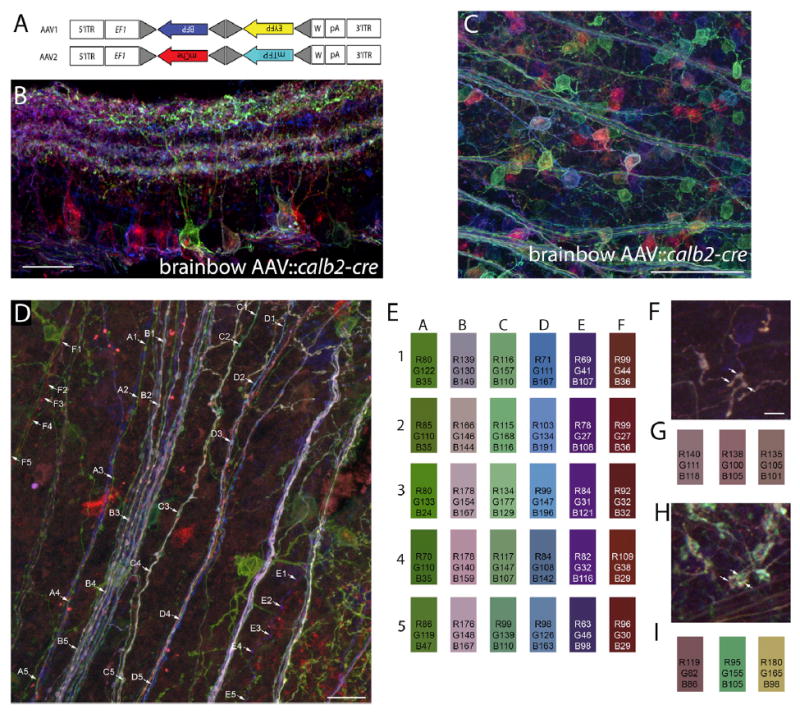
(A) Schematic representing the constructs of each of the two brainbow AAVs used in these studies. Following Cre recombination, these two constructs generate either farnesylated Tag-blue fluorescent protein (BFP) or enhanced yellow fluorescent protein (EYFP), or monomeric Cherry fluorescent protein (mChe) or monomeric teal fluorescent protein (mTFP). EF1 represent regulatory elements from the elongation 1α gene and W represents elements from the woodchuck hepatitis virus posttranscriptional regulatory element. Lox site mutants are depicted with gray triangles. For additional details, see Cai et al. (2013).
(B) Confocal image of a P35 retinal cross-section following intraocular injection of brainbow AAV into calb2-cre mice. Note the ability to delineate the dendritic arbor of the green-labeled RGC from adjacent fluorescently labeled RGCs.
(C) Confocal image of a P35 retinal whole mount following intraocular injection of brainbow AAV into calb2-cre mice.
(D) Confocal image of differentially labeled RGC axons in a P35 retinal whole-mount brainbow AAV∷calb2-cre mouse.
(E) Color analysis at five locations (1–5) along the six axons labeled in (D) (labeled A–F). The color boxes represent the colors at each point highlighted along the axons. Numbers in the boxes represent the red (R), green (G), and blue (B) color intensity values at each point along the axons. Note the relative similar distribution of “color” along each axon.
(F and G) A single retinal axon labeled with brainbow AAVs in the “core” region of dLGN of a P35 calb2-cre mouse. (G) Color analysis for the three boutons highlighted by arrows in (F).
(H and I) Terminals from three distinct retinal axons converging at a single cluster following labeling with brainbow AAVs in the “core” region of dLGN of a P35 calb2-cre mouse. (I) Color analysis for the three boutons highlighted in (H).
Scale bar in (B), 50 μm, in (D), 50 μm, in (C), 100 μm and in (F), 6 μm for (F) and (H).
