Figure 4. Ultrastructural Analysis and Reconstruction of Retinal Axons Contributing to “Complex Encapsulated” Retinogeniculate Synapses in dLGN.
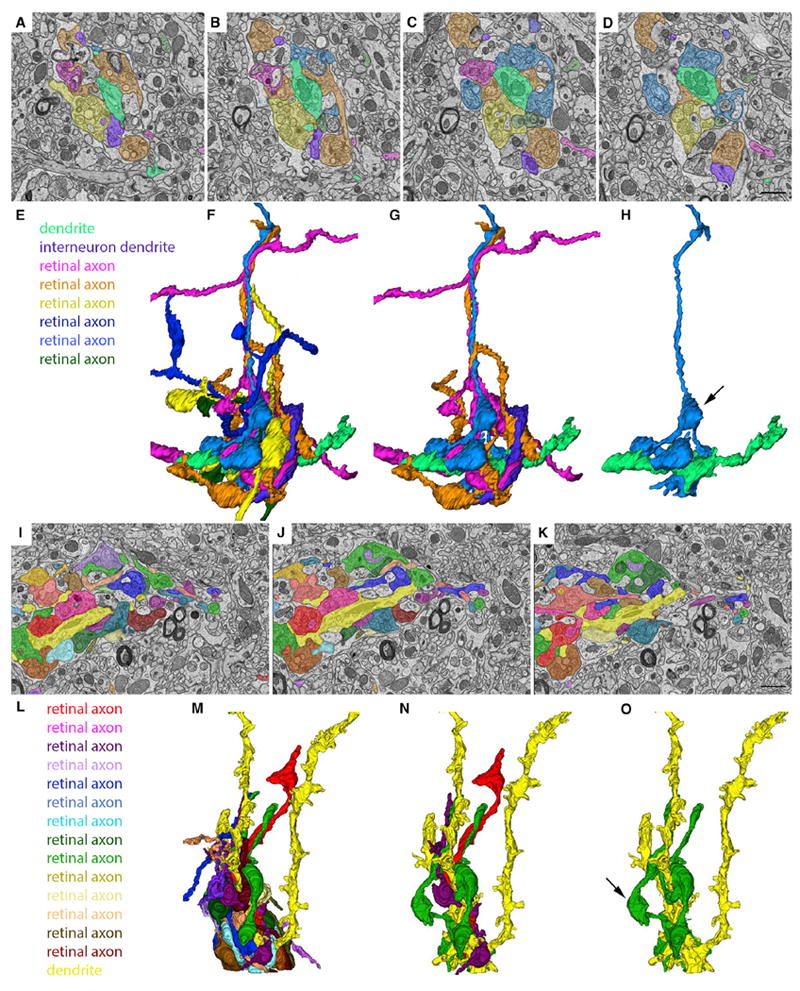
(A–D) SBFSEM images of six retinal terminals synapsing onto the same relay cell dendrite (pseudo-colored in bright green) in the “shell” region of dLGN.
(E) Key indicates the types of cellular elements pseudo-colored in (A)–(D) and (F)–(H).
(F) 3D reconstruction of all of the elements pseudo-colored in (A)–(D).
(G) 3D reconstruction of three RGC axons, an inhibitory interneuron dendrite and the relay cell dendrite in (A)–(D).
(H) 3D reconstruction of a single RGC axon and the relay cell dendrite in (A)–(D). Arrow indicates a retinal bouton that makes synaptic contact with an element other than the relay cell dendrite pseudo-colored bright green.
(I–K) SBFSEM images of 14 retinal terminals synapsing onto the same relay cell dendrite (pseudo-colored in bright yellow).
(L) Key indicates the types of cellular elements pseudo-colored in (I)–(K) and (M)–(O).
(M) 3D reconstruction of all of the elements pseudo-colored in (I)–(K).
(N) 3D reconstruction of three RGC axons and the relay cell dendrite in (I)–(K).
(O) 3D reconstruction of a single RGC axon and the relay cell dendrite in (I)–(K). Arrow indicates a retinal bouton that makes synaptic contact with an element other than the relay cell dendrite pseudo-colored bright yellow. Scale bar in (D), 1.5 μm for (A)–(D), and in (K), 1.5 μm for (I)–(K).
