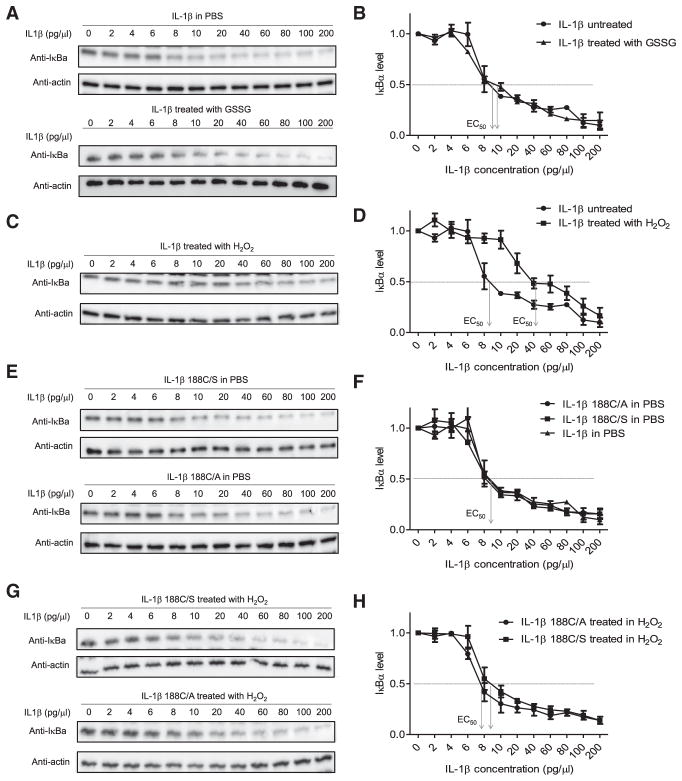
Figure 2. H2O2, but Not Cysteine S-Glutathionylation, Induces Cys-188-Dependent IL-1β Deactivation.
(A) The effect of glutathionylation on IL-β were pretreated with or without GSSG (250 μM) for 1 hr at 37°C before adding to HeLa cell cultures. Figures are representative of at least three independent experiments.
(B) Densitometry results expressed as ratios to the value of untreated cells (PBS alone). Results are the means (±SD) of three independent experiments. The IL-1β concentration inducing half the maximal response (EC50) is indicated.
(C) The effect of H2O2-induced oxidation on IL-1β bioactivity assessed by the IκB degradation assay. Indicated amounts of IL-1β were pretreated with H2O2 (100 μM) for one h at 37°C before adding to HeLa cell cultures.
(D) Densitometry results (means ±SD of three independent experiments).
(E) Bioactivity of mutant forms of IL-1β assessed by the IκB degradation assay. Representative immunoblots are shown.
(F) Densitometry results (means ±SD of three independent experiments).
(G) The effect of H2O2-induced oxidation on the bioactivity of mutant IL-1β assessed by the IκB degradation assay. Indicated amounts of mutant IL-1β were pretreated with or without H2O2 (100 μM) for one hr at 37°C before adding to HeLa cell cultures. Representative immunoblots for IκBα are shown.
(H) Densitometry results (means ±SD of three independent experiments). EC50 for each mutant IL-1β are indicated.