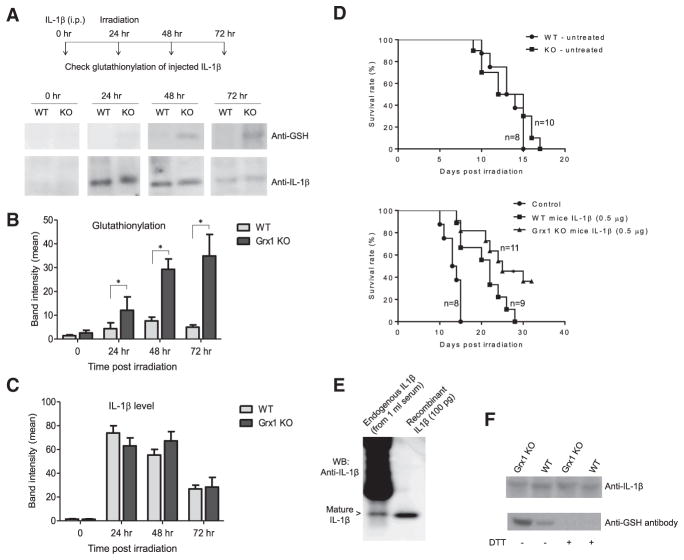
Figure 7. Grx1 Is a Physiological Regulator of IL-1β Cysteine S-Glutathionylation and IL-1β Bioactivity.
(A) S-glutathionylation of i.p.-injected recombinant IL-1β in WT and Grx1 KO mice detected by western blotting. His-tagged recombinant mouse IL-β in WT and Grx1 KO mice was detected by western blotting. His-tagged recombinant mouse IL-1β (1 μg/mouse) was injected i.p. 24 hr before γ-irradiation. Recombinant IL-1β was pulled down from the serum using Ni-NTA agarose beads at the times indicated.
(B) Quantitative analysis of protein glutathionylation. Densitometry of the blots performed using ImageJ software. Results are the means ±SD of three independent experiments. *p ≤ 0.005 versus WT.
(C) Quantitative analysis of total IL-1β protein level.
(D) Kaplan-Meier survival curves showing that disruption of Grx1 augments IL-1β bioactivity in mice. Recombinant mouse IL-1β (0.5 μg/mouse) was administered i.p. 20 hr before irradiation. *p ≤ 0.005 versus WT mice, log-rank test.
(E) S-glutathionylation of endogenously produced IL-1β. Mice were challenged with LPS (10 mg/kg, i.p. injection). The serum was collected 6 hr post-injection. Endogenously produced IL-1β in the serum (1 mL, pooled from three mice) was immunoprecipitated using Hamster anti-IL-1β mAb (clone B122).
(F) Disruption of Grx1 augmented S-glutathionylation of endogenously produced IL-1β. The experiment was conducted as described above. Samples were treated with or without DTT (10 mM) before loading onto the SDS-PAGE.