Figure 4.
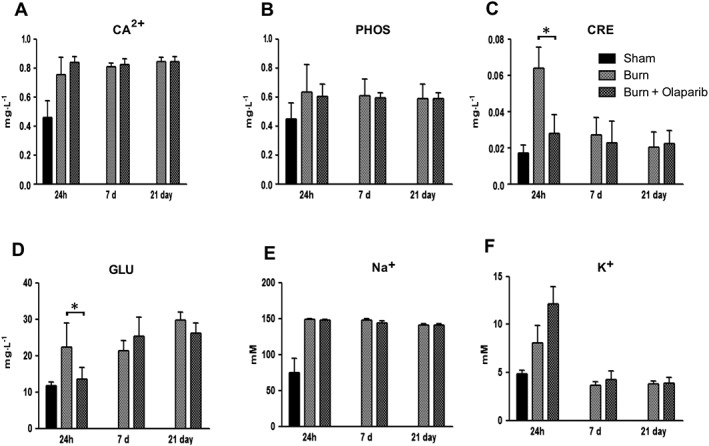
Effect of olaparib treatment on burn‐induced increases in selected parameters of organ injury. Various physiological and organ injury marker levels (plasma calcium [Ca2+], plasma phosphate [PHOS], plasma creatinine [CRE], plasma glucose [GLU], plasma sodium [Na+] and plasma potassium [K+]) are shown in sham‐control mice and in mice subjected to burn injury and in burn mice treated with olaparib (10 mg·kg−1, i.p.) once a day for 1 day, 6 days and 20 days. Compared to non‐burn sham control, burn produced a significant increase (P < 0.05) in calcium and sodium levels at all three time points studied and in creatinine, glucose and potassium levels at 24 h. Significant effect of olaparib on creatinine and glucose levels during burn injury is shown at 24 h (*P < 0.05). Data are shown as mean ± SEM of 10 animals for each group.
