Figure 6. The CB1 positive allosteric modulator GAT211 does not produce tolerance typical of MGL inhibitor JZL184 in paclitaxel-treated mice or induce physical dependence.
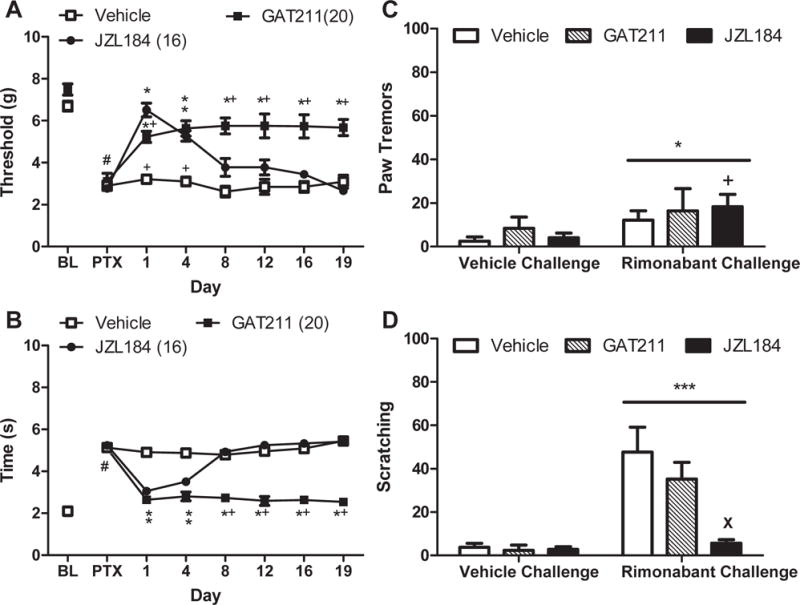
GAT211 (20 mg/kg i.p. × 19 days) suppressed paclitaxel-induced (A) mechanical and (B) cold allodynia throughout the entire 19 day dosing period relative to vehicle. JZL184 (16 mg/kg × 19 days i.p.) suppressed paclitaxel-induced (A) mechanical and (B) cold allodynia but tolerance developed by day 8 of chronic dosing. When challenged with vehicle, mice treated chronically with GAT211 (20 mg/kg/day i.p. × 20 days) or JZL184 (16 mg/kg/day i.p. × 20 days) did not exhibit (C) paw tremors or (D) scratching behaviors. (C,D) Rimonabant challenge did not induce withdrawal behaviors in either GAT211-treated or vehicle-treated mice but reduced the numbers of scratching bouts in mice treated with JZL184. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n=4-6 per group). (A),(B)*P<0.05 vs. vehicle, +P<0.05 vs. JZL184 one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test. #P<0.05 vs. pre-paclitaxel baseline, repeated measures ANOVA. (C),(D) *P<0.05 vs. vehicle challenge, two-way ANOVA. +P<0.05 JZL184 Rimonabant Challenge vs. JZL184 vehicle challenge, paired t-test. XP<0.05 vs vehicle, two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-hoc test.
