Figure 4.
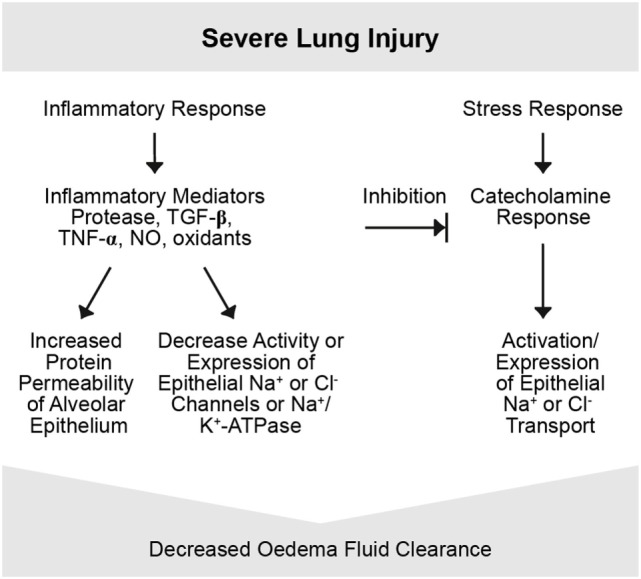
Severe lung injury. Severe lung injury may usually lead to decreased edema clearance. Severe injury usually includes alveolar epithelial injury and, thus, increases epithelial permeability and electrolytes and is associated with reduced epithelial Na+ transport. Inflammatory mediators are involved in this response, such as proteases, tumor necrosis factor (TNF), TGF-β, nitric oxide (NO), and oxidants. Possibly the intensity of the inflammatory response may transform a mild to a severe lung injury form by inducing changes in function and integrity of the alveolar epithelium and endothelium (4).
