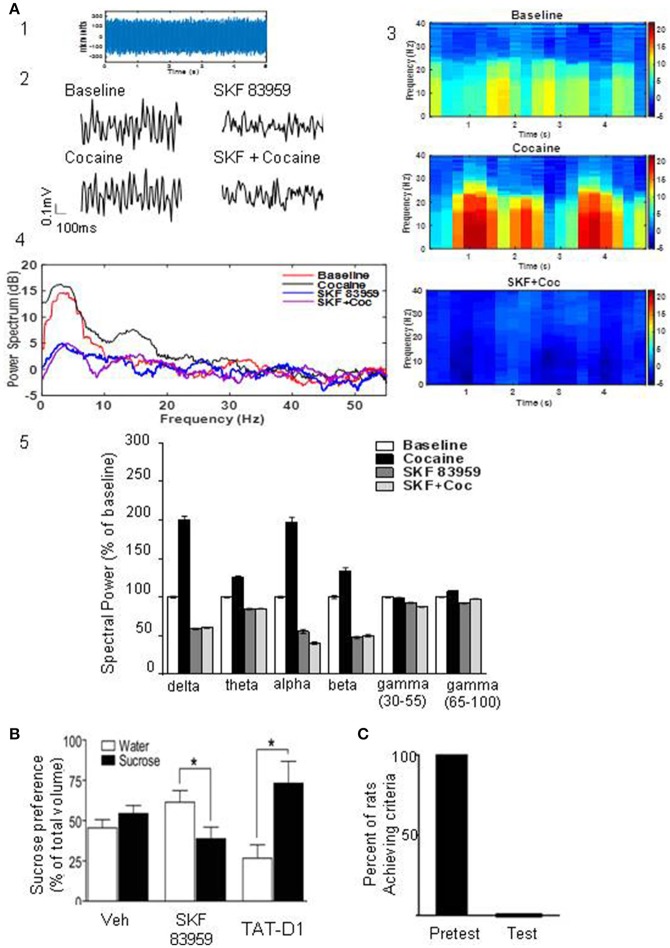
Figure 6.
Heteromer D1-D2 activation inhibits cocaine-induced changes in LFPs and modulates food reward. (A) Analysis of local field potentials (LFPs) from a sample 5 s epoch of baseline LFP recordings derived from rat NAc (A1). Representative 100 ms LFP amplitude recordings of baseline and recordings derived from rat NAc treated with cocaine, SKF 83959 or both drugs (A2). Spectrograms depicting time-frequency analysis showing the relative change in power of specific frequencies across the 5 s epoch of rats treated with cocaine or cocaine + SKF 83959 in comparison to the baseline (A3). Representative power spectrum showing acute cocaine induced increase in spectral power at lower frequencies (<30 Hz) which was suppressed by pretreatment with SKF 83959 (A4). Drug-induced changes in mean spectral power at select frequencies are also shown (A5). (B) Sucrose preference test. A single injection of SKF 83959 in a two bottle free choice paradigm significantly decreased the proportion of sucrose consumed but had no effect on water consumed (1st and 2nd set of bars). Administration of TAT-D1 (300 pmoles i.c.v) significantly increased the proportion of sucrose consumed (3rd set of bars). Results represent the mean ± SEM from 8 to 9 rats/condition. *p < 0.05 represents significant difference from control. (C) Activation of the D1-D2 heteromer abolished the motivation of rats to search for and consume a palatable sweet treat. Rats that had been successfully trained (pretest) were administered a single injection of SKF 83959 (1.5 mg/kg s.c.), placed in the radial arm maze and the number of trials required to reach the set criteria (11 consecutive correct choices) were documented. In each animal tested (Test), SKF 83959 abolished the motivation of the animals to search for and consume the food reward.